Page 149 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 149
136 Chapter 3
spring at its connection point to the mass. Compare the maximum rotation
angle of a constant rectangular cross-section beam when w = 5 t with the
maximum rotation angle of a right elliptic microhinge having the same length
and minimum width with the constant cross-section design, and a root
parameter b = 1/5.
Solution:
The maximum rotation angle generated by a torsion hinge is:
The ratio of the maximum rotation angle for a constant rectangular cross-
section spring to the similar rotation angle corresponding to a right elliptic
microhinge is:
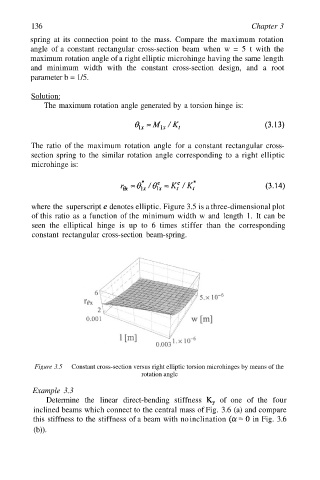
where the superscript denotes elliptic. Figure 3.5 is a three-dimensional plot
of this ratio as a function of the minimum width w and length 1. It can be
seen the elliptical hinge is up to 6 times stiffer than the corresponding
constant rectangular cross-section beam-spring.
Figure 3.5 Constant cross-section versus right elliptic torsion microhinges by means of the
rotation angle
Example 3.3
Determine the linear direct-bending stiffness of one of the four
inclined beams which connect to the central mass of Fig. 3.6 (a) and compare
this stiffness to the stiffness of a beam with no inclination in Fig. 3.6
(b)).