Page 152 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 152
3. Microsuspensions 139
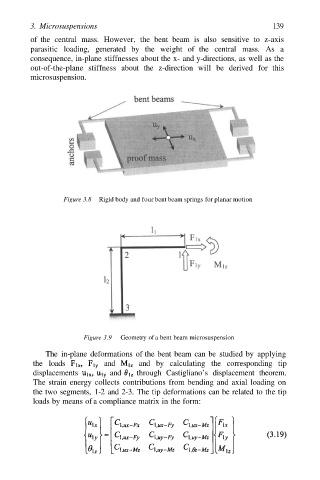
of the central mass. However, the bent beam is also sensitive to z-axis
parasitic loading, generated by the weight of the central mass. As a
consequence, in-plane stiffnesses about the x- and y-directions, as well as the
out-of-the-plane stiffness about the z-direction will be derived for this
microsuspension.
Figure 3.8 Rigid body and four bent beam springs for planar motion
Figure 3.9 Geometry of a bent beam microsuspension
The in-plane deformations of the bent beam can be studied by applying
the loads and and by calculating the corresponding tip
displacements and through Castigliano’s displacement theorem.
The strain energy collects contributions from bending and axial loading on
the two segments, 1-2 and 2-3. The tip deformations can be related to the tip
loads by means of a compliance matrix in the form: