Page 113 -
P. 113
3.3 Experimental Measurement and Comparison 103
90
80
Sphere
Incident angle (deg) 60 3 4 5
70
2
Radius
(mm)
50
40
30
9 10
8
20 7
6
10
0 5 10
Off-axial distance (mm)
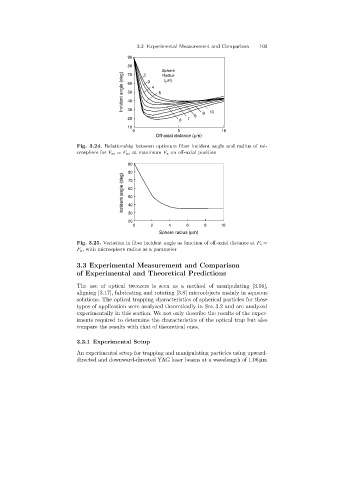
Fig. 3.24. Relationship between optimum fiber incident angle and radius of mi-
crosphere for F sz = F gz at maximum F g on off-axial position
90
80
Incident angle (deg) 70
60
50
40
30
20
0 2 4 6 8 10
Sphere radius (mm)
Fig. 3.25. Variation in fiber incident angle as function of off-axial distance at F s =
F g, with microsphere radius as a parameter
3.3 Experimental Measurement and Comparison
of Experimental and Theoretical Predictions
The use of optical tweezers is seen as a method of manipulating[3.16],
aligning[3.17], fabricatingand rotating[3.8] microobjects mainly in aqueous
solutions. The optical trappingcharacteristics of spherical particles for these
types of application were analyzed theoretically in Sec. 3.2 and are analyzed
experimentally in this section. We not only describe the results of the exper-
iments required to determine the characteristics of the optical trap but also
compare the results with that of theoretical ones.
3.3.1 Experimental Setup
An experimental setup for trappingand manipulatingparticles usingupward-
directed and downward-directed YAG laser beams at a wavelength of 1.06 µm