Page 117 -
P. 117
3.3 Experimental Measurement and Comparison 107
0.40
Minimum trapping power (mW) 0.30 Experimental
0.35
0.25
Beam waist
0.20
Ray optics
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
0 2 4 6 8
Particle diameter (mm)
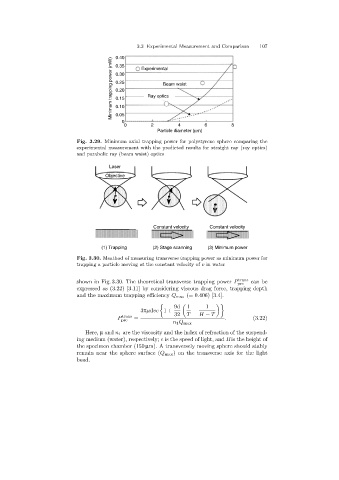
Fig. 3.29. Minimum axial trapping power for polystyrene sphere comparing the
experimental measurement with the predicted results for straight ray (ray optics)
and parabolic ray (beam waist)optics
Laser
Objective
Constant velocity Constant velocity
(1) Trapping (2) Stage scanning (3) Minimum power
Fig. 3.30. Meathod of measuring transverse trapping power as minimum power for
trapping a particle moving at the constant velocity of v in water
trans
shown in Fig. 3.30. The theoretical transverse trapping power P pre can be
expressed as (3.22) [3.11] by consideringviscous dragforce, trappingdepth
and the maximum trappingefficiency Q max (= 0.406) [3.4].
9d 1 1
3πµdvc 1+ −
32 T H − T
trans
P pre = . (3.22)
n 1 Q max
Here, µ and n 1 are the viscosity and the index of refraction of the suspend-
ingmedium (water), respectively; c is the speed of light, and His the height of
the specimen chamber (150 µm). A transversely movingsphere should stably
remain near the sphere surface (Q max ) on the transverse axis for the light
bead.