Page 145 -
P. 145
4.2 Theoretical Analysis I – Optical Torque 135
Laser
Slope
Rotation
III
II
III
I
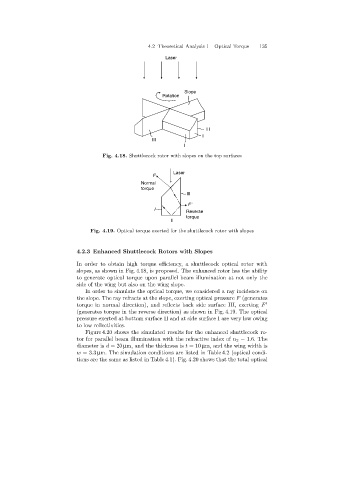
Fig. 4.18. Shuttlecock rotor with slopes on the top surfaces
Laser
F
Normal
torque
III
F
I
Reverse
torque
II
Fig. 4.19. Optical torque exerted for the shuttlecock rotor with slopes
4.2.3 Enhanced Shuttlecock Rotors with Slopes
In order to obtain high torque efficiency, a shuttlecock optical rotor with
slopes, as shown in Fig. 4.18, is proposed. The enhanced rotor has the ability
to generate optical torque upon parallel beam illumination at not only the
side of the wingbut also on the wingslope.
In order to simulate the optical torque, we considered a ray incidence on
the slope. The ray refracts at the slope, exertingoptical pressure F (generates
torque in normal direction), and reflects back side surface III, exerting F
(generates torque in the reverse direction) as shown in Fig. 4.19. The optical
pressure exerted at bottom surface II and at side surface I are very low owing
to low reflectivities.
Figure 4.20 shows the simulated results for the enhanced shuttlecock ro-
tor for parallel beam illumination with the refractive index of n 2 =1.6. The
diameter is d =20 µm, and the thickness is t =10 µm, and the wingwidth is
w =3.3 µm. The simulation conditions are listed in Table 4.2 (optical condi-
tions are the same as listed in Table 4.1). Fig. 4.20 shows that the total optical