Page 215 -
P. 215
5.4 Future Applications 205
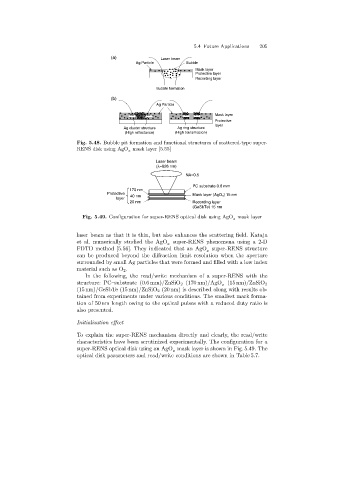
(a) Laser beam
Ag Particle Bubble
Mask layer
Protective layer
Recording layer
Bubble formation
(b)
Ag Particle
Mask layer
Protective
layer
Ag cluster structure Ag ring structure
(High reflectance) (High transmission)
Fig. 5.48. Bubble pit formation and functional structures of scattered-type super-
RENS disk using AgO mask layer [5.55]
x
Laser beam
(l=826 nm)
NA=0.5
PC substrate 0.6 mm
170 nm
Protective
40 nm Mask layer (AgO x) 15 nm
layer
20 nm Recording layer
(GeSbTe) 15 nm
Fig. 5.49. Configuration for super-RENS optical disk using AgO mask layer
x
laser beam as that it is thin, but also enhances the scatteringfield. Kataja
et al. numerically studied the AgO super-RENS phenomena usinga 2-D
x
FDTD method [5.56]. They indicated that an AgO super-RENS structure
x
can be produced beyond the diffraction limit resolution when the aperture
surrounded by small Agparticles that were formed and filled with a low index
material such as O 2 .
In the following, the read/write mechanism of a super-RENS with the
structure: PC–substrate (0.6 mm)/ZnSiO 2 (170 nm)/AgO (15 nm)/ZnSiO 2
x
(15 nm)/GeSbTe (15 nm)/ZnSiO 2 (20 nm) is described alongwith results ob-
tained from experiments under various conditions. The smallest mark forma-
tion of 50 nm length owing to the optical pulses with a reduced duty ratio is
also presented.
Initialization effect
To explain the super-RENS mechanism directly and clearly, the read/write
characteristics have been scrutinized experimentally. The configuration for a
super-RENS optical disk usingan AgO mask layer is shown in Fig. 5.49. The
x
optical disk parameters and read/write conditions are shown in Table 5.7.