Page 103 - Modern Control Systems
P. 103
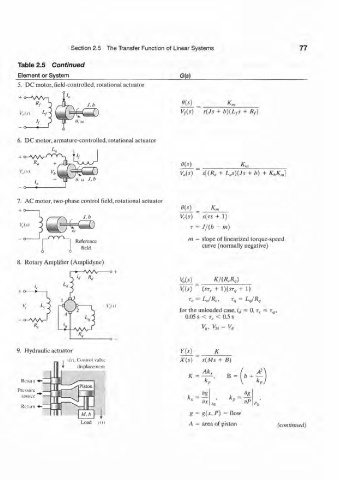
Section 2.5 The Transfer Function of Linear Systems 77
Table 2.5 Continued
Element or System G(s)
5. DC motor, field-controlled, rotational actuator
V f{s) s(Js + b){L fs + R f)
6. DC motor, armature-controlled, rotational actuator
m _ K*
V a(s) s[(R a + L as)(Js + b) + K hK,„]
7. AC motor, two-phase control field, rotational actuator
+ o 9{») ._ K„
V c(s) S{TS + 1)
^04=G3
V,(.u T = J/(b - m)
in = slope of linearized torque-speed
Reference
curve (normally negative)
field
8. Rotary Amplifier (Amplidyne)
>—Wv o +
K/(W
V C(S) (ST C + 1 ) ( - , + 1)
for the unloaded case, l d ~ 0, r c T,M
0.05 s < T C < 0.5 s
9. Hydraulic actt ator Yls) K
n t • c(ft. Control valve X(s) s(Ms + *)
displacement
Ak x
Return •*- •-K)
Piston
* • k - - i
V V
Return •*- "0
TV M, h i g = g(x,P) = flow
L oad A = are a of jiston (continued)