Page 174 - Modern Spatiotemporal Geostatistics
P. 174
Uncertainty Assessment 155
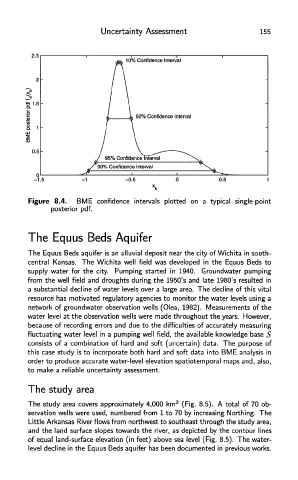
Figure 8.4. BME confidence intervals plotted on a typical single-point
posterior pdf.
The Equus Beds Aquifer
The Equus Beds aquifer is an alluvial deposit near the city of Wichita in south-
central Kansas. The Wichita well field was developed in the Equus Beds to
supply water for the city. Pumping started in 1940. Groundwater pumping
from the well field and droughts during the 1950's and late 1980's resulted in
a substantial decline of water levels over a large area. The decline of this vital
resource has motivated regulatory agencies to monitor the water levels using a
network of groundwater observation wells (Olea, 1982). Measurements of the
water level at the observation wells were made throughout the years. However,
because of recording errors and due to the difficulties of accurately measuring
fluctuating water level in a pumping well field, the available knowledge base S
consists of a combination of hard and soft (uncertain) data. The purpose of
this case study is to incorporate both hard and soft data into BME analysis in
order to produce accurate water-level elevation spatiotemporal maps and, also,
to make a reliable uncertainty assessment.
The study area
The study area covers approximately 4,000 km 2 (Fig. 8.5). A total of 70 ob-
servation wells were used, numbered from 1 to 70 by increasing Northing. The
Little Arkansas River flows from northwest to southeast through the study area,
and the land surface slopes towards the river, as depicted by the contour lines
of equal land-surface elevation (in feet) above sea level (Fig. 8.5). The water-
level decline in the Equus Beds aquifer has been documented in previous works.