Page 259 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 259
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 4 CONTROL OF NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
moved, the revolution pitch, which is the welding The revolution pitch is the distance over which the
speed V divided by the rotation speed N, can be an tool moves while the tool rotates one time, and is
index for the heat input. equivalent to the interval of the lines formed on the
surface of the welded part after FSW. A higher revo-
/
Rotation pitch VN (4.5.2) lution pitch, namely, greater movement during one
rotation, indicates a lower heat input. In FSW, the
quantity of the heat input is one of the important
290 parameters, which determines the success or failure
Normal grained steel of the welding or friction stir process [8].
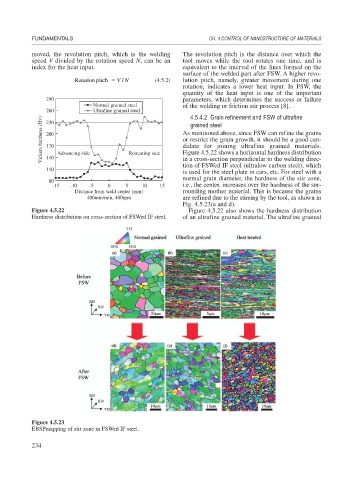
260 Ultrafine grained steel 4.5.4.2 Grain refinement and FSW of ultrafine
Vickers hardness (Hv) 200 Advancing side Retreating side As mentioned above, since FSW can refine the grains
230
grained steel
or restrict the grain growth, it should be a good can-
didate for joining ultrafine grained materials.
170
Figure 4.5.22 shows a horizontal hardness distribution
140
in a cross-section perpendicular to the welding direc-
tion of FSWed IF steel (ultralow carbon steel), which
110
is used for the steel plate in cars, etc. For steel with a
normal grain diameter, the hardness of the stir zone,
80
-15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 i.e., the center, increases over the hardness of the sur-
Distance from weld center (mm) rounding mother material. This is because the grains
400mm/min, 400rpm are refined due to the stirring by the tool, as shown in
Fig. 4.5.23(a and d).
Figure 4.5.22 Figure 4.5.22 also shows the hardness distribution
Hardness distribution on cross-section of FSWed IF steel. of an ultrafine grained material. The ultrafine grained
Figure 4.5.23
EBSPmapping of stir zone in FSWed IF steel.
234