Page 453 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 453
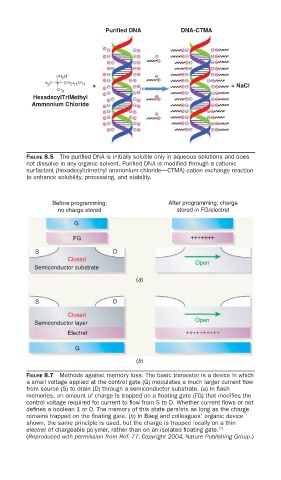
Purified DNA DNA-CTMA
–
CH Cl
3
+
H C N (CH ) 2 15 CH 3 + + NaCl
3
CH
3
HexadecylTriMethyl
Ammonium Chloride
FIGURE 8.5 The purifi ed DNA is initially soluble only in aqueous solutions and does
not dissolve in any organic solvent. Purifi ed DNA is modifi ed through a cationic
surfactant (hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium chloride––CTMA) cation exchange reaction
to enhance solubility, processing, and stability.
Before programming; After programming; charge
no charge stored stored in FG/electret
G
FG +++++++
S D
Closed
Open
Semiconductor substrate
(a)
S D
Closed
Open
Semiconductor layer
Electret ++++++++++
G
(b)
FIGURE 8.7 Methods against memory loss. The basic transistor is a device in which
a small voltage applied at the control gate (G) modulates a much larger current fl ow
from source (S) to drain (D) through a semiconductor substrate. (a) In fl ash
memories, an amount of charge is trapped on a fl oating gate (FG) that modifi es the
control voltage required for current to fl ow from S to D. Whether current fl ows or not
defi nes a boolean 1 or 0. The memory of this state persists as long as the charge
remains trapped on the fl oating gate. (b) In Baeg and colleagues’ organic device
shown, the same principle is used, but the charge is trapped locally on a thin
electret of chargeable polymer, rather than on an isolated fl oating gate. 73
(Reproduced with permission from Ref. 77. Copyright 2004, Nature Publishing Group.)