Page 320 - Plastics Engineering
P. 320
Processing of Plastics 303
area mouldings such as car bumpers and body panels. Another consequence
of the low injection pressures is that mould materials other than steel may
be considered. Aluminium has been used successfully and this permits weight
savings in large moulds. Moulds are also less expensive than injection moulds
but they must not be regarded as cheap. RIM moulds require careful design
and, in particular, a good surface finish because the expansion of the material
in the mould during polymerisation causes every detail on the surface of the
mould to be reproduced on the moulding.
4.3.9 Injection Blow Moulding
In Section 4.2.7 we considered the process of extrusion blow moulding which
is used to produce hollow articles such as bottles. At that time it was mentioned
that if molecular orientation can be introduced to the moulding then the prop-
erties are significantly improved. In recent years the process of injection blow
moulding has been developed to achieve this objective. It is now very widely
used for the manufacture of bottles for soft drinks.
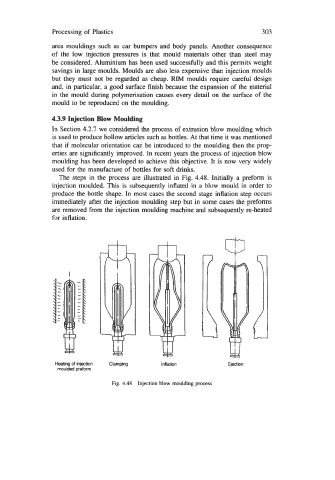
The steps in the process are illustrated in Fig. 4.48. Initially a preform is
injection moulded. This is subsequently inflated in a blow mould in order to
produce the bottle shape. In most cases the second stage inflation step occurs
immediately after the injection moulding step but in some cases the preforms
are removed from the injection moulding machine and subsequently re-heated
for inflation.
.i
I
Heating of injection Clamping Inflation Ejection
moulded preform
Fig. 4.48 Injection blow moulding process