Page 351 - Plastics Engineering
P. 351
334 Processing of Plastics
Y P P fibres of
l
Y
Supply of
', p,rotated (b)
Heated
mould
Exhaust \ \ \
fan Preform \, 63
transferred \ /p
(a) to mould \,,
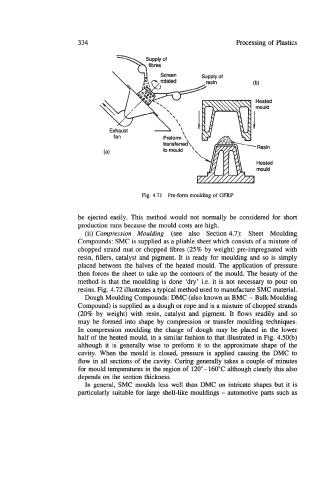
Fig. 4.71 Re-form moulding of GFRP
be ejected easily. This method would not normally be considered for short
production runs because the mould costs are high.
(ii) Compression Moulding (see also Section 4.7): Sheet Moulding
Compounds: SMC is supplied as a pliable sheet which consists of a mixture of
chopped strand mat or chopped fibres (25% by weight) pre-impregnated with
resin, fillers, catalyst and pigment. It is ready for moulding and so is simply
placed between the halves of the heated mould. The application of pressure
then forces the sheet to take up the contours of the mould. The beauty of the
method is that the moulding is done 'dry' i.e. it is not necessary to pour on
resins. Fig. 4.72 illustrates a typical method used to manufacture SMC material.
Dough Moulding Compounds: DMC (also known as BMC - Bulk Moulding
Compound) is supplied as a dough or rope and is a mixture of chopped strands
(20% by weight) with resin, catalyst and pigment. It flows readily and so
may be formed into shape by compression or transfer moulding techniques.
In compression moulding the charge of dough may be placed in the lower
half of the heated mould, in a similar fashion to that illustrated in Fig. 4.50(b)
although it is generally wise to preform it to the approximate shape of the
cavity. When the mould is closed, pressure is applied causing the DMC to
flow in all sections of the cavity. Curing generally takes a couple of minutes
for mould temperatures in the region of 12W-160"C although clearly this also
depends on the section thickness.
In general, SMC moulds less well than DMC on intricate shapes but it is
particularly suitable for large shell-like mouldings - automotive parts such as