Page 131 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 131
118 S. Yuvarajan
one type, called the P-channel MCT, has been widely reported Anode
and is discussed here. Because the gate of the device is referred
to with respect to the anode rather than the cathode, it is
Metal Metal
sometimes referred to as a complementary MCT (C-MCT)
[2]. Harris Semiconductors (Intersil) originally made the Oxide Oxide
MCTs, but the MCT division was sold to Silicon Power Gate Gate
Corporation (SPCO), which has continued the development Gate
of MCTs. n+ n+
p+
p p
8.2 Equivalent Circuit and Switching
Characteristics n(pnp base, Off-FET drain)
The SCR is a 4-layer pnpn device with a control gate, and
applying a positive gate pulse turns it on when it is forward-
biased. The regenerative action in the device helps to speed up p-(npn base, On-FET drain)
the turn-on process and to keep it in the ‘‘ON'' state even after
the gate pulse is removed. The MCT uses an auxiliary MOS
p buffer, epitaxial layer
device (PMOSFET) to turn on and this simpli®es the gate
control. The turn-on has all the characteristics of a power
MOSFET. The turn-off is accomplished using another
n+ substrate
Metal
Cathode
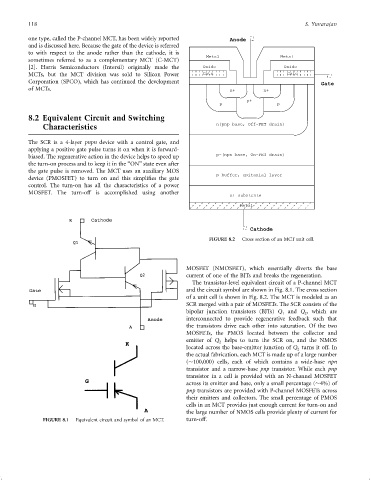
FIGURE 8.2 Cross section of an MCT unit cell.
MOSFET (NMOSFET), which essentially diverts the base
current of one of the BJTs and breaks the regeneration.
The transistor-level equivalent circuit of a P-channel MCT
and the circuit symbol are shown in Fig. 8.1. The cross section
of a unit cell is shown in Fig. 8.2. The MCT is modeled as an
SCR merged with a pair of MOSFETs. The SCR consists of the
bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) Q and Q , which are
1
2
interconnected to provide regenerative feedback such that
the transistors drive each other into saturation. Of the two
MOSFETs, the PMOS located between the collector and
emitter of Q helps to turn the SCR on, and the NMOS
2
located across the base-emitter junction of Q turns it off. In
2
the actual fabrication, each MCT is made up of a large number
( 100,000) cells, each of which contains a wide-base npn
transistor and a narrow-base pnp transistor. While each pnp
transistor in a cell is provided with an N-channel MOSFET
across its emitter and base, only a small percentage ( 4%) of
pnp transistors are provided with P-channel MOSFETs across
their emitters and collectors. The small percentage of PMOS
cells in an MCT provides just enough current for turn-on and
the large number of NMOS cells provide plenty of current for
FIGURE 8.1 Equivalent circuit and symbol of an MCT. turn-off.