Page 192 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 192
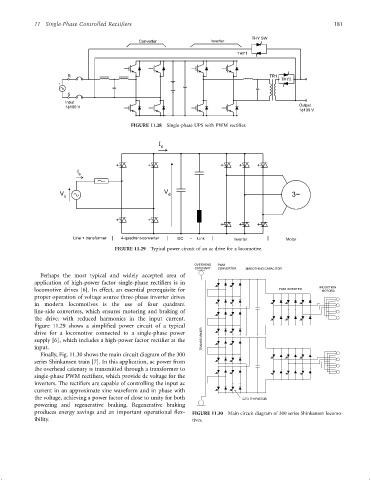
11 Single-Phase Controlled Recti®ers 181
THY SW
Converter Inverter
THY1
R TR1
THY2
+
S
Input
1f100 V Output
1f100 V
FIGURE 11.28 Single-phase UPS with PWM recti®er.
I
d
i
s
V V d 3~
s
Line + transformer 4-quadrant-converter DC - Link Inverter Motor
FIGURE 11.29 Typical power circuit of an ac drive for a locomotive.
OVERHEAD PWM
CATENARY CONVERTER SMOOTHING CAPACITOR
Perhaps the most typical and widely accepted area of
application of high-power factor single-phase recti®ers is in
INDUCTION
locomotive drives [6]. In effect, an essential prerequisite for PWM INVERTER MOTORS
proper operation of voltage source three-phase inverter drives
in modern locomotives is the use of four quadrant
line-side converters, which ensures motoring and braking of
the drive, with reduced harmonics in the input current.
Figure 11.29 shows a simpli®ed power circuit of a typical
drive for a locomotive connected to a single-phase power
supply [6], which includes a high-power factor recti®er at the TRANSFORMER
input.
Finally, Fig. 11.30 shows the main circuit diagram of the 300
series Shinkansen train [7]. In this application, ac power from
the overhead catenary is transmitted through a transformer to
single-phase PWM recti®ers, which provide dc voltage for the
inverters. The recti®ers are capable of controlling the input ac
current in an approximate sine waveform and in phase with
the voltage, achieving a power factor of close to unity for both GTO THYRISTOR
powering and regenerative braking. Regenerative braking
produces energy savings and an important operational ¯ex- FIGURE 11.30 Main circuit diagram of 300 series Shinkansen locomo-
ibility. tives.