Page 262 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 262
14 Inverters 251
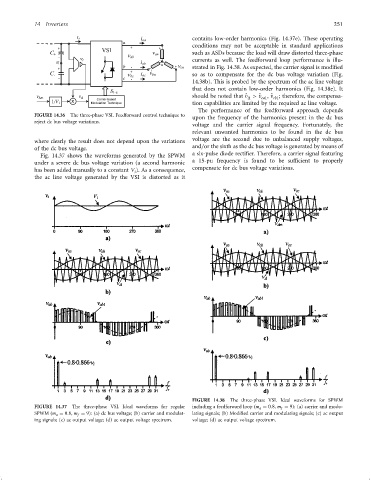
contains low-order harmonics (Fig. 14.37e). These operating
conditions may not be acceptable in standard applications
such as ASDs because the load will draw distorted three-phase
currents as well. The feedforward loop performance is illu-
strated in Fig. 14.38. As expected, the carrier signal is modi®ed
so as to compensate for the dc bus voltage variation (Fig.
14.38b). This is probed by the spectrum of the ac line voltage
that does not contain low-order harmonics (Fig. 14.38e). It
should be noted that ^ v > ^ v , ^ v ; therefore, the compensa-
D
cb1
ca1
tion capabilities are limited by the required ac line voltage.
The performance of the feedforward approach depends
FIGURE 14.36 The three-phase VSI. Feedforward control technique to
upon the frequency of the harmonics present in the dc bus
reject dc bus voltage variations.
voltage and the carrier signal frequency. Fortunately, the
relevant unwanted harmonics to be found in the dc bus
voltage are the second due to unbalanced supply voltages,
where clearly the result does not depend upon the variations
and=or the sixth as the dc bus voltage is generated by means of
of the dc bus voltage.
a six-pulse diode recti®er. Therefore, a carrier signal featuring
Fig. 14.37 shows the waveforms generated by the SPWM
a 15-pu frequency is found to be suf®cient to properly
under a severe dc bus voltage variation (a second harmonic
compensate for dc bus voltage variations.
has been added manually to a constant V ). As a consequence,
i
the ac line voltage generated by the VSI is distorted as it
FIGURE 14.38 The three-phase VSI. Ideal waveforms for SPWM
FIGURE 14.37 The three-phase VSI. Ideal waveforms for regular including a feedforward loop ðm a ¼ 0:8, m f ¼ 9): (a) carrier and modu-
SPWM ðm a ¼ 0:8, m f ¼ 9): (a) dc bus voltage; (b) carrier and modulat- lating signals; (b) Modi®ed carrier and modulating signals; (c) ac output
ing signals; (c) ac output voltage; (d) ac output voltage spectrum. voltage; (d) ac output voltage spectrum.