Page 93 - Rashid, Power Electronics Handbook
P. 93
6 The Power MOSFET 79
i implementation using a power switch whose switching
sw
+ waveforms are shown in Fig. 6.4a; (b) derive the expres-
sions for the instantaneous switching and conduction
v
sw power losses and sketch them; (c) determine the total
average power dissipated in the circuit during one
_
switching frequency; and (d) determine the maximum
v power.
sw
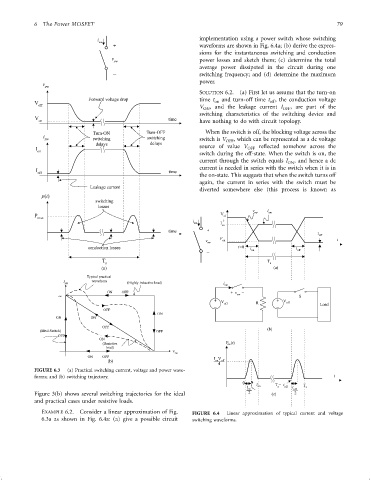
SOLUTION 6.2. (a) First let us assume that the turn-on
Forward voltage drop time t and turn-off time t , the conduction voltage
V on off
off V , and the leakage current I , are part of the
ON OFF
switching characteristics of the switching device and
V time
on have nothing to do with circuit topology.
i Turn-ON Turn-OFF When the switch is off, the blocking voltage across the
sw switching switching switch is V OFF , which can be represented as a dc voltage
delays delays
I source of value V OFF re¯ected somehow across the
on
switch during the off-state. When the switch is on, the
current through the switch equals I ON , and hence a dc
current is needed in series with the switch when it is in
I time
off
the on-state. This suggests that when the switch turns off
again, the current in series with the switch must be
Leakage current
diverted somewhere else (this process is known as
p(t)
switching
losses
v sw i sw
P V of
max
i f
sw I
on
time +
I off
v V on t
sw
conduction losses t=0 t t
_ on off
T T
s s
(a) (a)
Typical practical
i waveform
sw (Highly Inductive load) i
sw
ON OFF + v -
ON sw S
V off R V off Load
OFF
ON
ON ON
OFF
(Ideal Switch) OFF (b)
OFF
ON
(Resistive P sw ()t
load)
v
sw
ON OFF I V
(b) on off
4
FIGURE 6.3 (a) Practical switching current, voltage and power wave-
forms; and (b) switching trajectory. t
0 t T - t T
t on s off t s
on off
Figure 3(b) shows several switching trajectories for the ideal 2 (c) 2
and practical cases under resistive loads.
EXAMPLE 6.2. Consider a linear approximation of Fig. FIGURE 6.4 Linear approximation of typical current and voltage
6.3a as shown in Fig. 6.4a: (a) give a possible circuit switching waveforms.