Page 199 - Renewable Energy Devices and System with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS
P. 199
186 Renewable Energy Devices and Systems with Simulations in MATLAB and ANSYS ®
®
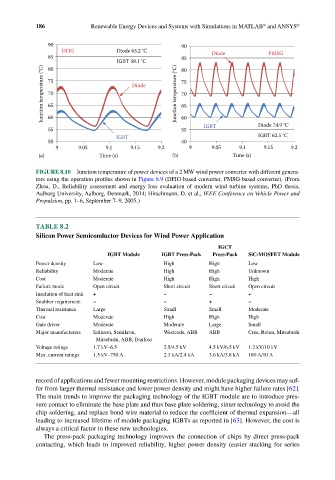
90 90
DFIG Diode 63.2 °C Diode PMSG
85 85
IGBT 58.1 °C 80
80
Junction temperature (°C) 75 Diode Junction temperature (°C) 75
70
70
65
65
60
55 60 IGBT Diode 74.9 °C
55
IGBT IGBT 62.5 °C
50 50
9 9.05 9.1 9.15 9.2 9 9.05 9.1 9.15 9.2
(a) Time (s) (b) Time (s)
FIGURE 8.10 Junction temperature of power devices of a 2 MW wind power converter with different genera-
tors using the operation profiles shown in Figure 8.9 (DFIG-based converter, PMSG-based converter). (From
Zhou, D., Reliability assessment and energy loss evaluation of modern wind turbine systems, PhD thesis,
Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2014; Hirschmann, D. et al., IEEE Conference on Vehicle Power and
Propulsion, pp. 1–6, September 7–9, 2005.)
TABLE 8.2
Silicon Power Semiconductor Devices for Wind Power Application
IGCT
IGBT Module IGBT Press-Pack Press-Pack SiC-MOSFET Module
Power density Low High High Low
Reliability Moderate High High Unknown
Cost Moderate High High High
Failure mode Open circuit Short circuit Short circuit Open circuit
Insulation of heat sink + − − +
Snubber requirement − − + −
Thermal resistance Large Small Small Moderate
Cost Moderate High High High
Gate driver Moderate Moderate Large Small
Major manufacturers Infineon, Semikron, Westcode, ABB ABB Cree, Rohm, Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi, ABB, Danfoss
Voltage ratings 1.7 kV–6.5 2.5/4.5 kV 4.5 kV/6.5 kV 1.2 kV/10 kV
Max. current ratings 1.5 kV–750 A 2.3 kA/2.4 kA 3.6 kA/3.8 kA 180 A/10 A
record of applications and fewer mounting restrictions. However, module packaging devices may suf-
fer from larger thermal resistance and lower power density and might have higher failure rates [62].
The main trends to improve the packaging technology of the IGBT module are to introduce pres-
sure contact to eliminate the base plate and thus base plate soldering, sinter technology to avoid the
chip soldering, and replace bond wire material to reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion—all
leading to increased lifetime of module packaging IGBTs as reported in [63]. However, the cost is
always a critical factor in these new technologies.
The press-pack packaging technology improves the connection of chips by direct press-pack
contacting, which leads to improved reliability, higher power density (easier stacking for series