Page 86 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits
P. 86
AMPLIFIERS AND OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS
CHAP. 5]
5.9 DIFFERENTIAL AND DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIERS 75
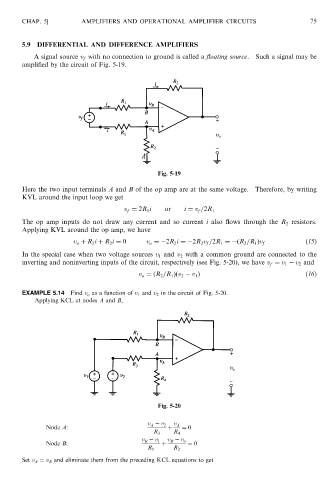
A signal source v f with no connection to ground is called a floating source. Such a signal may be
amplified by the circuit of Fig. 5-19.
Fig. 5-19
Here the two input terminals A and B of the op amp are at the same voltage. Therefore, by writing
KVL around the input loop we get
v f ¼ 2R 1 i or i ¼ v f =2R 1
The op amp inputs do not draw any current and so current i also flows through the R 2 resistors.
Applying KVL around the op amp, we have
v o þ R 2 i þ R 2 i ¼ 0 v o ¼ 2R 2 i ¼ 2R 2 v f =2R 1 ¼ ðR 2 =R 1 Þv f ð15Þ
In the special case when two voltage sources v 1 and v 2 with a common ground are connected to the
inverting and noninverting inputs of the circuit, respectively (see Fig. 5-20), we have v f ¼ v 1 v 2 and
v o ¼ðR 2 =R 1 Þðv 2 v 1 Þ ð16Þ
EXAMPLE 5.14 Find v o as a function of v 1 and v 2 in the circuit of Fig. 5-20.
Applying KCL at nodes A and B,
Fig. 5-20
v A v 2 v A
Node A: þ ¼ 0
R 3 R 4
v B v 1 v B v o
Node B: þ ¼ 0
R 1 R 2
Set v A ¼ v B and eliminate them from the preceding KCL equations to get