Page 181 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 181
Geng(SMH)_CH13.qxd 04/04/2005 19:50 Page 13.4
PHYSICAL VAPOR DEPOSITION
13.4 WAFER PROCESSING
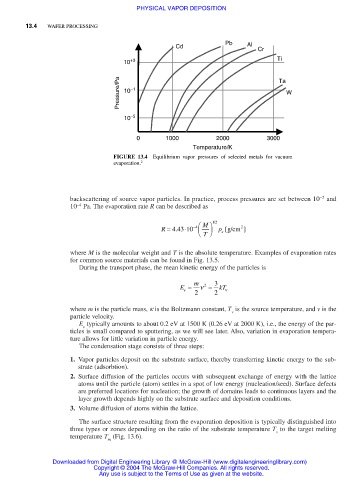
Pb Al
Cd
Cr
10 +3 Ti
Pressure/Pa 10 −1 Ta W
10 −5
0 1000 2000 3000
Temperature/K
FIGURE 13.4 Equilibrium vapor pressures of selected metals for vacuum
evaporation. 2
backscattering of source vapor particles. In practice, process pressures are set between 10 −2 and
−4
10 Pa. The evaporation rate R can be described as
M 12 /
.
R = 443 ⋅10 −4 p [g/cm 2 ]
T s
where M is the molecular weight and T is the absolute temperature. Examples of evaporation rates
for common source materials can be found in Fig. 13.5.
During the transport phase, the mean kinetic energy of the particles is
E = m n 2 = 3 kT
e
2 2 n
where m is the particle mass, k is the Boltzmann constant, T is the source temperature, and v is the
v
particle velocity.
E typically amounts to about 0.2 eV at 1500 K (0.26 eV at 2000 K), i.e., the energy of the par-
e
ticles is small compared to sputtering, as we will see later. Also, variation in evaporation tempera-
ture allows for little variation in particle energy.
The condensation stage consists of three steps:
1. Vapor particles deposit on the substrate surface, thereby transferring kinetic energy to the sub-
strate (adsorbtion).
2. Surface diffusion of the particles occurs with subsequent exchange of energy with the lattice
atoms until the particle (atom) settles in a spot of low energy (nucleation/seed). Surface defects
are preferred locations for nucleation; the growth of domains leads to continuous layers and the
layer growth depends highly on the substrate surface and deposition conditions.
3. Volume diffusion of atoms within the lattice.
The surface structure resulting from the evaporation deposition is typically distinguished into
three types or zones depending on the ratio of the substrate temperature T to the target melting
s
temperature T (Fig. 13.6).
m
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.