Page 185 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 185
Geng(SMH)_CH13.qxd 04/04/2005 19:51 Page 13.8
PHYSICAL VAPOR DEPOSITION
13.8 WAFER PROCESSING
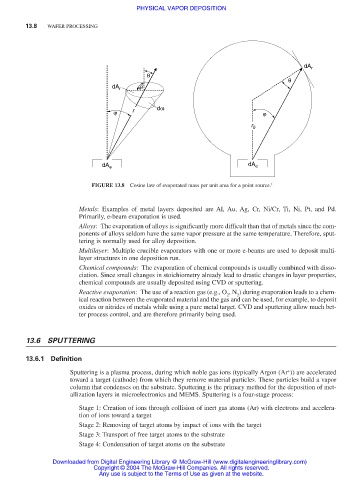
dA r
θ
θ
dA r 90°
dω
ϕ r ϕ
r 0
dA e dA e
FIGURE 13.8 Cosine law of evaporated mass per unit area for a point source. 1
Metals: Examples of metal layers deposited are Al, Au, Ag, Cr, Ni/Cr, Ti, Ni, Pt, and Pd.
Primarily, e-beam evaporation is used.
Alloys: The evaporation of alloys is significantly more difficult than that of metals since the com-
ponents of alloys seldom have the same vapor pressure at the same temperature. Therefore, sput-
tering is normally used for alloy deposition.
Multilayer: Multiple crucible evaporators with one or more e-beams are used to deposit multi-
layer structures in one deposition run.
Chemical compounds: The evaporation of chemical compounds is usually combined with disso-
ciation. Since small changes in stoichiometry already lead to drastic changes in layer properties,
chemical compounds are usually deposited using CVD or sputtering.
Reactive evaporation: The use of a reaction gas (e.g., O , N ) during evaporation leads to a chem-
2
2
ical reaction between the evaporated material and the gas and can be used, for example, to deposit
oxides or nitrides of metals while using a pure metal target. CVD and sputtering allow much bet-
ter process control, and are therefore primarily being used.
13.6 SPUTTERING
13.6.1 Definition
+
Sputtering is a plasma process, during which noble gas ions (typically Argon (Ar )) are accelerated
toward a target (cathode) from which they remove material particles. These particles build a vapor
column that condenses on the substrate. Sputtering is the primary method for the deposition of met-
allization layers in microelectronics and MEMS. Sputtering is a four-stage process:
Stage 1: Creation of ions through collision of inert gas atoms (Ar) with electrons and accelera-
tion of ions toward a target
Stage 2: Removing of target atoms by impact of ions with the target
Stage 3: Transport of free target atoms to the substrate
Stage 4: Condensation of target atoms on the substrate
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.