Page 141 - Separation process principles 2
P. 141
106 Chapter 3 Mass Transfer and Diffusion
The instantaneous mass-transfer rate for an eddy with an From (3-196), the residence-time distribution is given by
age t is given by (3-192) for the penetration theory in flux
form as
where t is in seconds. Equations (1) and (2) are plotted in
Figure 3.20. These curves are much different from the curves
of Figure 3.19.
The integrated average rate is
Film-Penetration Theory
Toor and Marchello [62], in 1958, combined features of the
film, penetration, and surface-renewal theories to develop a
Combining (3- 197), (3-198), and (3-199), and integrating: film-penetration model, which predicts a dependency of the
mass-transfer coefficient kc, on the diffusivity, that varies
from fi to DAB Their theory assumes that the entire re-
sistance to mass transfer resides in a film of fixed thickness
Thus,
6. Eddies move to and from the bulk fluid and this film. Age
distributions for time spent in the film are of the Higbie or
Danckwerts type.
The more reasonable surface-renewal theory predicts the Fick's second law, (3-68), still applies, but the boundary
same dependency of the mass-transfer coefficient on molec- conditions are now
ular diffusivity as the penetration theory. Unfortunately, s,
CA = CA~ at t = 0 for 0 5 z 5 GO,
the fractional rate of surface renewal, is as elusive a parame-
CA = CA, at z = 0 for t > 0; and
ter as the constant contact time, tc.
CA = CA~ at z = 6 for t > 0
Infinite-series solutions are obtained by the method of
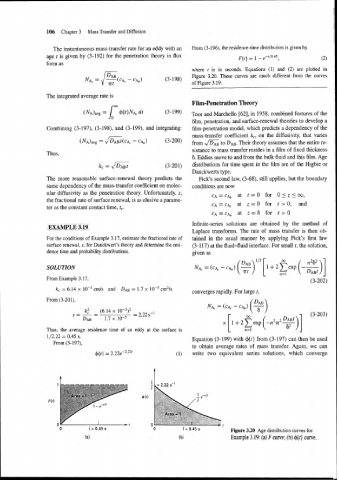
EXAMPLE 3.19
Laplace transforms. The rate of mass transfer is then ob-
For the conditions of Example 3.17, estimate the fractional rate of tained in the usual manner by applying Fick's first law
surface renewal, s, for Danckwert's theory and determine the resi- (3-1 17) at the fluid-fluid interface. For small t, the solution,
dence time and probability distributions. given as
SOLUTION
From Example 3.17,
kc = 6.14 x lop3 cmls and DAB = 1.7 x cm2/s
converges rapidly. For large t,
From (3-201),
Thus, the average residence time of an eddy at the surface is
112.22 = 0.45 s.
Equation (3-199) with +It] from (3-197) can then be used
From (3-197),
to obtain average rates of mass transfer. Again, we can
write two equivalent series solutions, which converge
1
FIII
0
0 7 = 0.45 s
Figure 3.20 Age distribution curves for
(a) (b) Example 3.19: (a) F curve: (b) $(t} curve.