Page 185 - Separation process principles 2
P. 185
150 Chapter 4 Single Equilibrium Stages and Flash Calculations
Constant pressure Constant pressure Dew point
Two liquid phases
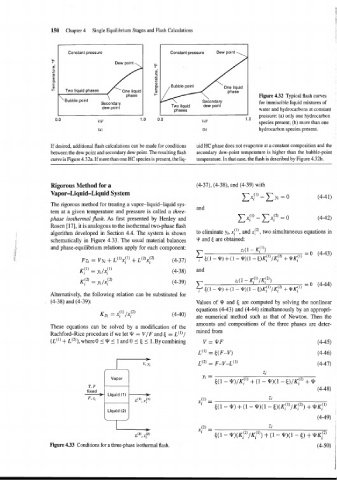
Figure 4.32 Typical flash curves
'Bubble point
Secondary for immiscible liquid mixtures of
dew point Two liquid dew point
phases water and hydrocarbons at constant
pressure: (a) only one hydrocarbon
1 .o
species present; (b) more than one
hydrocarbon species present.
If desired, additional flash calculations can be made for conditions uid HC phase does not evaporate at a constant composition and the
between the dew point and secondary dew point. The resulting flash secondary dew-point temperature is higher than the bubble-point
curve is Figure 4.32a. If more than one HC species is present, the liq- temperature. In that case, the flash is described by Figure 4.32b.
Rigorous Method for a (4-37), (4-38), and (4-39) with
Vapor-Liquid-Liquid System Ex:" -cy, (4-41)
=O
The rigorous method for treating a vapor-liquid-liquid sys-
and
tem at a given temperature and pressure is called a three-
phase isothermal flash. As first presented by Henley and c X/l) - c x(2) = 0 (4-42)
Rosen [17], it is analogous to the isothermal two-phase flash
algorithm developed in Section 4.4. The system is shown to eliminate y,, xj", and x:', two simultaneous equations in
schematically in Figure 4.33. The usual material balances q and 5 are obtained:
and phase-equilibrium relations apply for each component: zi(l - Kill)
C = 0 (4-43)
+
+
Fzi = Vyi + L(')~,(') L(~)~!~) (4-37) i t(1 - U1) + (1 - Y)(1 - ~)K~"/Kj2) OKJ~)
and
Alternatively, the following relation can be substituted for
(4-38) and (4-39): Values of Q and 6 are computed by solving the nonlinear
equations (4-43) and (4-44) simultaneously by an appropri-
ate numerical method such as that of Newton. Then the
amounts and compositions of the three phases are deter-
These equations can be solved by a modification of the
mined from
Rachford-Rice procedure if we let q = V/F and 6 = L(')/
(L(') + L(~)), where0 I 1 and 0 5 6 I 1.Bycombining V = QF (4-45)
5
Q
Vapor
T. P
fixed
Liquid (1)
F. Zi
1 Liquid (2) 1
Figure 4.33 Conditions for a three-phase isothermal flash.