Page 87 - Sustainability in the Process Industry Integration and Optimization
P. 87
64 Cha p te r F o u r
T* [°C] T* [°C]
300 300
750 750
900 900
300
200 200
300
400 400
100 100
1400 1400
1200 1200
1000 1000
0 500 1000 1500 0 2000 4000 6000 8000
Q [kW] ΔH [kW]
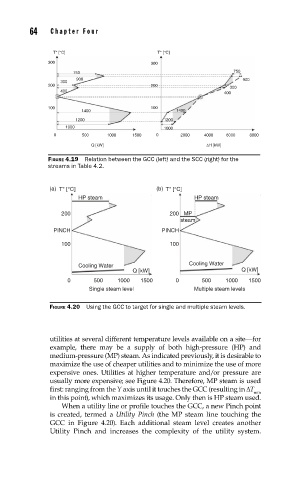
FIGURE 4.19 Relation between the GCC (left) and the SCC (right) for the
streams in Table 4.2.
(a) T* [°C] (b) T* [°C]
HP steam HP steam
200 200 MP
steam
PINCH PINCH
100 100
Cooling Water Cooling Water
Q [kW] Q [kW]
0 500 1000 1500 0 500 1000 1500
Single steam level Multiple steam levels
FIGURE 4.20 Using the GCC to target for single and multiple steam levels.
utilities at several different temperature levels available on a site—for
example, there may be a supply of both high-pressure (HP) and
medium-pressure (MP) steam. As indicated previously, it is desirable to
maximize the use of cheaper utilities and to minimize the use of more
expensive ones. Utilities at higher temperature and/or pressure are
usually more expensive; see Figure 4.20. Therefore, MP steam is used
first: ranging from the Y axis until it touches the GCC (resulting in ΔT
min
in this point), which maximizes its usage. Only then is HP steam used.
When a utility line or profile touches the GCC, a new Pinch point
is created, termed a Utility Pinch (the MP steam line touching the
GCC in Figure 4.20). Each additional steam level creates another
Utility Pinch and increases the complexity of the utility system.