Page 155 - The Geological Interpretation of Well Logs
P. 155
- THE NEUTRON LOG -
Evaporites
The neutron log can be used to distinguish between evap- z GR APL] pOaOsite %
orites on the basis of water of crystallization (Table 10.9). 3 |0 20080 20 10 9-10
a
Of the evaporites with water of crystallization, gypsum om
——3
(CaSO,.2H,O) is the most common. However, carnallite, Totty
polyhalite and kainite also contain the water radical (Table ee]
10.9). All these minerals have a high neutron-log value atta]
which differentiates them from other evaporites such as SALT | + + +]
salt (NaC1) or anhydrite (CaSO,), which contain no water ae a4
. + + +
and hence have a log value of zero (Figure 10.21). F**7
+ +» + 4
to oF o+
Identification of hydrated minerals CARNALLITE [ACace|
Hydrated minerals (excluding evaporites) are not com- AND SALT PECECE
mon. However, hydrated iron compounds may be shaly |+—+—+—4 100m
sufficiently abundant to affect the logs. Thus a zone of
coe
CARNALLITE | C C
c
c
Table 10.9 Neutron log values of some evaporites (from J
Schlumberger, 1985). cc OO
Cc Cc
Mineral Composition Neutron logValuet fot
+ + + 4
+ + +
Camalite KCIMgC1,.6H,O 60" . tt
+ + + 4
Py SOO to eo 5 sat fetes
ainite g50,KC1.3H, pre” 2000n
Polyhalite K,SO,MgSO, + + + 4
2CaSO,.2H,0 25 ted
Halite NaCi -3 cr
Anbydrite CaSO, -2 e
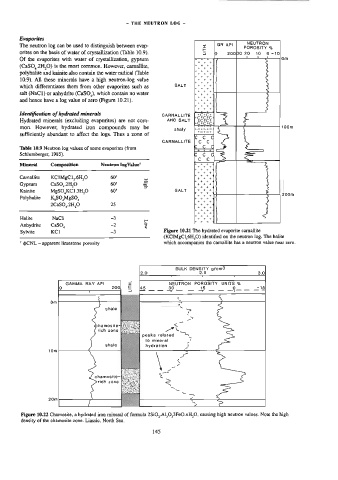
Sylvite KCI 3 Figure 10.21 The hydrated evaporite carnallite
(KCIMgCL6H,0) identified on the neutron log. The halite
* @CNL - apparent limestone porosity which accompanies the carnallite has a neutron value near zero.
BULK DENSITY g/cm?
2.0 2.5 3.0
GAMMA RAY API NEUTRON POROSITY UNITS %
0 200 30 6
—_—_——o— OT 1 x8)
T
<
>
om
5
shale ~
‘>
ichamosite- <7
rich zone ‘ a7
peaks related 7
to mineral -
shale hydration ,
10m
os
_f
oo
4
~~
=
~
™
~ Yo
4
20m
©
>
Figure 10.22 Chamosite, a hydrated iron mineral of formula 2SiO,.Al,0,3FeO.nH,O, causing high neutron values. Note the high
density of the chamosite zone. Liassic, North Sea.
145