Page 204 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 204
182
Water Distribution Systems: Components, Design, and Operation
Chapter 6
Static
Static
Average
Night
Average
Maximum
Maximum
Gravity flow
Static
A
Static
Average
Night
Maximum Double gravity flow Average
Static
B
Average Maximum
Maximum
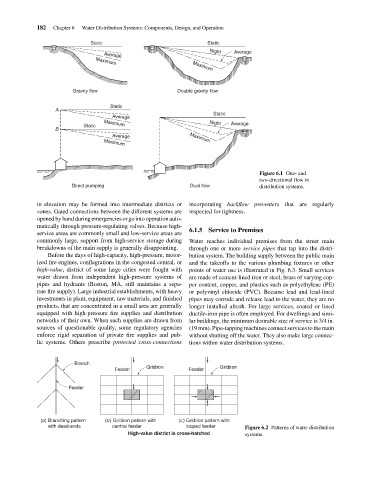
Figure 6.1 One- and
two-directional flow in
Direct pumping Dual flow distribution systems.
in elevation may be formed into intermediate districts or incorporating backflow preventers that are regularly
zones. Gated connections between the different systems are inspected for tightness.
opened by hand during emergencies or go into operation auto-
matically through pressure-regulating valves. Because high- 6.1.5 Service to Premises
service areas are commonly small and low-service areas are
commonly large, support from high-service storage during Water reaches individual premises from the street main
breakdowns of the main supply is generally disappointing. through one or more service pipes that tap into the distri-
Before the days of high-capacity, high-pressure, motor- bution system. The building supply between the public main
ized fire engines, conflagrations in the congested central, or and the takeoffs to the various plumbing fixtures or other
high-value, district of some large cities were fought with points of water use is illustrated in Fig. 6.3. Small services
water drawn from independent high-pressure systems of are made of cement-lined iron or steel, brass of varying cop-
pipes and hydrants (Boston, MA, still maintains a sepa- per content, copper, and plastics such as polyethylene (PE)
rate fire supply). Large industrial establishments, with heavy or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Because lead and lead-lined
investments in plant, equipment, raw materials, and finished pipes may corrode and release lead to the water, they are no
products, that are concentrated in a small area are generally longer installed afresh. For large services, coated or lined
equipped with high-pressure fire supplies and distribution ductile-iron pipe is often employed. For dwellings and simi-
networks of their own. When such supplies are drawn from lar buildings, the minimum desirable size of service is 3/4 in.
sources of questionable quality, some regulatory agencies (19 mm). Pipe-tapping machines connect services to the main
enforce rigid separation of private fire supplies and pub- without shutting off the water. They also make large connec-
lic systems. Others prescribe protected cross-connections tions within water distribution systems.
Branch
Feeder Gridiron Feeder Gridiron
Feeder
(a) Branching pattern (b) Gridiron pattern with (c) Gridiron pattern with
with dead-ends central feeder looped feeder Figure 6.2 Patterns of water distribution
High-value district is cross-hatched systems.