Page 205 - Water Engineering Hydraulics, Distribution and Treatment
P. 205
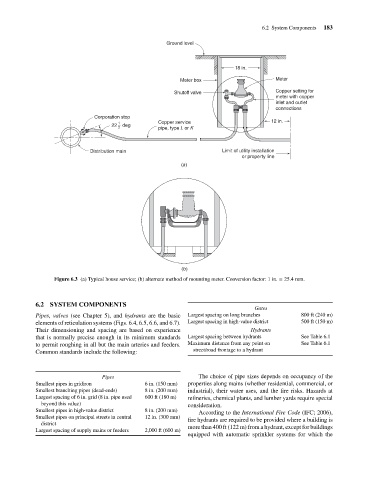
Ground level
Meter
Meter box
Copper setting for
Shutoff valve
meter with copper
inlet and outlet
connections
Corporation stop
12 in.
1
22 deg Copper service 18 in. 6.2 System Components 183
2 pipe, type L or K
Distribution main Limit of utility installation
or property line
(a)
(b)
Figure 6.3 (a) Typical house service; (b) alternate method of mounting meter. Conversion factor: 1 in. = 25.4 mm.
6.2 SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Gates
Pipes, valves (see Chapter 5), and hydrants are the basic Largest spacing on long branches 800 ft (240 m)
elements of reticulation systems (Figs. 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, and 6.7). Largest spacing in high-value district 500 ft (150 m)
Their dimensioning and spacing are based on experience Hydrants
that is normally precise enough in its minimum standards Largest spacing between hydrants See Table 6.1
to permit roughing in all but the main arteries and feeders. Maximum distance from any point on See Table 6.1
Common standards include the following: street/road frontage to a hydrant
Pipes The choice of pipe sizes depends on occupancy of the
Smallest pipes in gridiron 6 in. (150 mm) properties along mains (whether residential, commercial, or
Smallest branching pipes (dead-ends) 8 in. (200 mm) industrial), their water uses, and the fire risks. Hazards at
Largest spacing of 6 in. grid (8 in. pipe used 600 ft (180 m) refineries, chemical plants, and lumber yards require special
beyond this value) consideration.
Smallest pipes in high-value district 8 in. (200 mm)
According to the International Fire Code (IFC; 2006),
Smallest pipes on principal streets in central 12 in. (300 mm)
fire hydrants are required to be provided where a building is
district
more than 400 ft (122 m) from a hydrant, except for buildings
Largest spacing of supply mains or feeders 2,000 ft (600 m)
equipped with automatic sprinkler systems for which the