Page 1077 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1077
Table 11.14. Comparison of Computed and Observed E (kcal/mol) 1061
a
for Reaction of Halomethanes with Cl.
TOPIC 11.2
∗∗
Compound E a (MP4/6-31G ) E a (observed)
Structure-Reactivity
Relationships in
CH 3 F 3.4 1.54 ± 1.0
Hydrogen Abstraction
3.7 3.26 ± 1.0
CH 2 F 2
Reactions
9.7 7.62 ± .16
CHF 3
CH 3 Cl 3.9 2.50 ± 0.4
1.6 2.7 ± 1.0
CH 2 Cl 2
0.6 2.48 ± 1.0
CHCl 3
CH 2 CF 2.6 2.78 ± 1.0
5.4 4.51 ± 1.0
CHClF 2
CHCl 2 F 2.3
The purpose of this study was to test the reliability of theoretical rate calculations to
predict the atmospheric lifetime, an important property of these compounds:
X Y Z
HO . + CH X Y Z HO–H + CH n–1 o p q
n o p q
These kinetic data lead to a quadratic rather than linear Bell-Evans-Polyani relationship:
2
−3
ln k 298 = 1 368×10 H −0 354 H −50 96
The corresponding plot is shown in Figure 11.20.
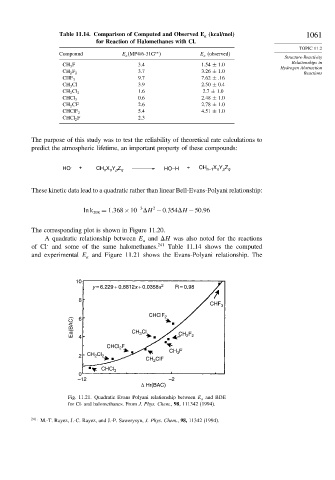
A quadratic relationship between E and H was also noted for the reactions
a
. 241
of Cl and some of the same halomethanes. Table 11.14 shows the computed
and experimental E and Figure 11.21 shows the Evans-Polyani relationship. The
a
10
y = 6.229 + 0.8812x + 0.0358x 2 R = 0.98
8
CHF 3
CHClF 2
Ea(BAC) 4 CH Cl CH 2 2
6
3
F
F
CHCl 2
CH F
3
2 CH Cl 2
2
CH 2 ClF
CHCl 3
0
–12 –2
Δ Hr(BAC)
Fig. 11.21. Quadratic Evans Polyani relationship between E a and BDE
for Cl· and halomethanes. From J. Phys. Chem., 98, 111342 (1994).
241
M.-T. Rayez, J.-C. Rayez, and J.-P. Sawerysyn, J. Phys. Chem., 98, 11342 (1994).