Page 1078 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1078
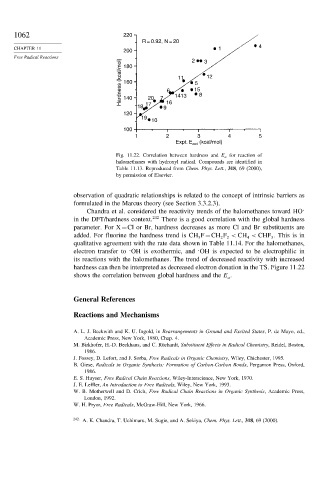
1062 220
R = 0.92, N = 20
4
CHAPTER 11 1
200
Free Radical Reactions 180 2 3
Hardness (kcal/mol) 160 6 11 15 12
5
20
140
18 17 7 9 16 1413 8
120
19
10
100
1 2 3 4 5
Expt. E act (kcal/mol)
Fig. 11.22. Correlation between hardness and E a for reaction of
halomethanes with hydroxyl radical. Compounds are identified in
Table 11.13. Reproduced from Chem. Phys. Lett., 318, 69 (2000),
by permission of Elsevier.
observation of quadratic relationships is related to the concept of intrinsic barriers as
formulated in the Marcus theory (see Section 3.3.2.3).
.
Chandra et al. considered the reactivity trends of the halomethanes toward HO
in the DFT/hardness context. 242 There is a good correlation with the global hardness
parameter. For X=Cl or Br, hardness decreases as more Cl and Br substituents are
added. For fluorine the hardness trend is CH F=CH F < CH < CHF . This is in
2 2
4
3
3
qualitative agreement with the rate data shown in Table 11.14. For the halomethanes,
.
.
electron transfer to OH is exothermic, and OH is expected to be electrophilic in
its reactions with the halomethanes. The trend of decreased reactivity with increased
hardness can then be interpreted as decreased electron donation in the TS. Figure 11.22
shows the correlation between global hardness and the E .
a
General References
Reactions and Mechanisms
A. L. J. Beckwith and K. U. Ingold, in Rearrangements in Ground and Excited States, P. de Mayo, ed.,
Academic Press, New York, 1980, Chap. 4.
M. Birkhofer, H.-D. Beckhaus, and C. Rüchardt, Substituent Effects in Radical Chemistry, Reidel, Boston,
1986.
J. Fossey, D. Lefort, and J. Sorba, Free Radicals in Organic Chemistry, Wiley, Chichester, 1995.
B. Giese, Radicals in Organic Synthesis: Formation of Carbon-Carbon Bonds, Pergamon Press, Oxford,
1986.
E. S. Huyser, Free Radical Chain Reactions, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1970.
J. E. Leffler, An Introduction to Free Radicals, Wiley, New York, 1993.
W. B. Motherwell and D. Crich, Free Radical Chain Reactions in Organic Synthesis, Academic Press,
London, 1992.
W. H. Pryor, Free Radicals, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1966.
242
A. K. Chandra, T. Uchimaru, M. Sugie, and A. Sekiya, Chem. Phys. Lett., 318, 69 (2000).