Page 1125 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1125
1110
CHAPTER 12
Photochemistry
A S 1
E S 0
A'
C
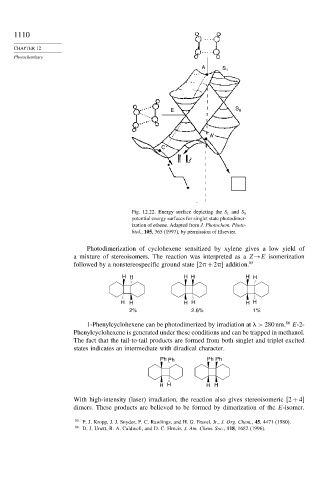
Fig. 12.22. Energy surface depicting the S 1 and S 0
potential energy surfaces for singlet state photodimer-
ization of ethene. Adapted from J. Photochem. Photo-
biol., 105, 365 (1997), by permission of Elsevier.
Photodimerization of cyclohexene sensitized by xylene gives a low yield of
a mixture of stereoisomers. The reaction was interpreted as a Z→E isomerization
followed by a nonstereospecific ground state [2 +2 ] addition. 85
H H H H H H
H H H H H H
2% 2.6% 1%
86
1-Phenylcyclohexene can be photodimerized by irradiation at > 280nm. E-2-
Phenylcyclohexene is generated under these conditions and can be trapped in methanol.
The fact that the tail-to-tail products are formed from both singlet and triplet excited
states indicates an intermediate with diradical character.
Ph Ph Ph Ph
H H H H
With high-intensity (laser) irradiation, the reaction also gives stereoisomeric [2 + 4]
dimers. These products are believed to be formed by dimerization of the E-isomer.
85 P. J. Kropp, J. J. Snyder, P. C. Rawlings, and H. G. Fravel, Jr., J. Org. Chem., 45, 4471 (1980).
86
D. J. Unett, R. A. Caldwell, and D. C. Hrncir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, 1682 (1996).