Page 200 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 200
172 These reagents usually react with aldehydes and ketones to give substituted alkenes
directly. No separate elimination step is necessary because fragmentation of the inter-
CHAPTER 2 mediate occurs spontaneously under the reaction conditions.
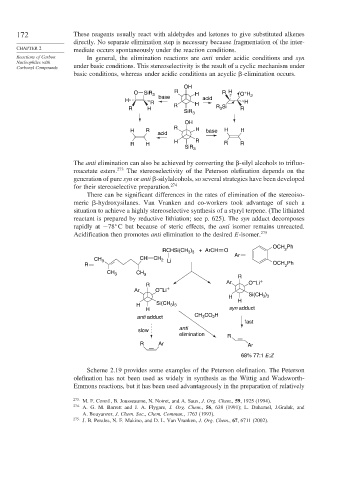
Reactions of Carbon In general, the elimination reactions are anti under acidic conditions and syn
Nucleophiles with
Carbonyl Compounds under basic conditions. This stereoselectivity is the result of a cyclic mechanism under
basic conditions, whereas under acidic conditions an acyclic -elimination occurs.
OH
+
O SiR 3 R H R H O H 2
H base acid
R H H
R H R R 3 Si R
SiR 3
OH
R
H R H base H H
acid
H R
R H R R
SiR 3
The anti elimination can also be achieved by converting the -silyl alcohols to trifluo-
roacetate esters. 273 The stereoselectivity of the Peterson olefination depends on the
generation of pure syn or anti -silylalcohols, so several strategies have been developed
for their stereoselective preparation. 274
There can be significant differences in the rates of elimination of the stereoiso-
meric -hydroxysilanes. Van Vranken and co-workers took advantage of such a
situation to achieve a highly stereoselective synthesis of a styryl terpene. (The lithiated
reactant is prepared by reductive lithiation; see p. 625). The syn adduct decomposes
rapidly at −78 C but because of steric effects, the anti isomer remains unreacted.
Acidification then promotes anti elimination to the desired E-isomer. 275
OCH Ph
) + ArCH O 2
RCHSi(CH 3 3
Ar
CH 3 CH CH 2 Li
R OCH Ph
2
CH 3 CH 3
R
– +
Ar O Li
R
– +
Ar O Li
Si(CH )
H 3 3
) H
H Si(CH 3 3
H syn adduct
CH CO H
anti adduct 3 2
fast
slow anti
elimination R
R Ar Ar
68% 77:1 E:Z
Scheme 2.19 provides some examples of the Peterson olefination. The Peterson
olefination has not been used as widely in synthesis as the Wittig and Wadsworth-
Emmons reactions, but it has been used advantageously in the preparation of relatively
273 M. F. Connil, B. Jousseaume, N. Noiret, and A. Saux, J. Org. Chem., 59, 1925 (1994).
274 A. G. M. Barrett and J. A. Flygare, J. Org. Chem., 56, 638 (1991); L. Duhamel, J.Gralak, and
A. Bouyanzer, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1763 (1993).
275
J. B. Perales, N. F. Makino, and D. L. Van Vranken, J. Org. Chem., 67, 6711 (2002).