Page 220 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 220
192
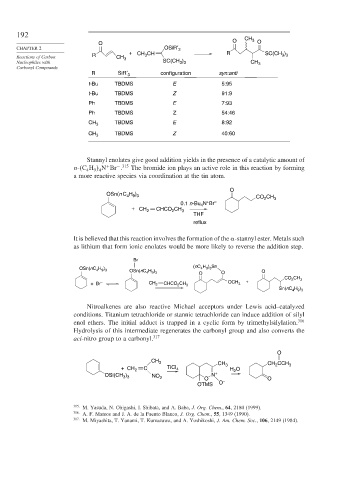
O CH 3 O
O
CHAPTER 2 OSiR′ 3
+ CH CH R )
R 3 SC(CH 3 3
Reactions of Carbon CH 3
Nucleophiles with SC(CH ) CH 3
3 3
Carbonyl Compounds
R SiR′ 3 configuration syn:anti
t-Bu TBDMS E 5:95
t-Bu TBDMS Z 91:9
Ph TBDMS E 7:93
Ph TBDMS Z 54:46
TBDMS E 8:92
CH 3
CH 3 TBDMS Z 40:60
Stannyl enolates give good addition yields in the presence of a catalytic amount of
− 315
n- C H N Br . The bromide ion plays an active role in this reaction by forming
+
9 4
4
a more reactive species via coordination at the tin atom.
O
OSn(n C H )
4 9 3
CO 2 CH 3
+
0.1 n-Bu 4 N Br –
+ CH 2 CHCO CH 3
2
THF
reflux
It is believed that this reaction involves the formation of the -stannyl ester. Metals such
as lithium that form ionic enolates would be more likely to reverse the addition step.
Br
(nC H ) Sn
OSn(nC H ) OSn(nC H ) 4 9 3
4 9 3
4 9 3 O O O
CH
CO 2 3
+ Br – CH 2 CHCO CH 3 OCH 3 +
2
Sn(nC H )
4 9 3
Nitroalkenes are also reactive Michael acceptors under Lewis acid–catalyzed
conditions. Titanium tetrachloride or stannic tetrachloride can induce addition of silyl
enol ethers. The initial adduct is trapped in a cyclic form by trimethylsilylation. 316
Hydrolysis of this intermediate regenerates the carbonyl group and also converts the
aci-nitro group to a carbonyl. 317
O
CH 3 CH 2 CCH
+ CH 2 C TiCl 4 CH 3 H 2 O 3
OSi(CH ) NO 2 O N + O
3 3
OTMS O –
315 M. Yasuda, N. Ohigashi, I. Shibata, and A. Baba, J. Org. Chem., 64, 2180 (1999).
316 A. F. Mateos and J. A. de la Fuento Blanco, J. Org. Chem., 55, 1349 (1990).
317
M. Miyashita, T. Yanami, T. Kumazawa, and A. Yoshikoshi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 106, 2149 (1984).