Page 236 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 236
Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
214
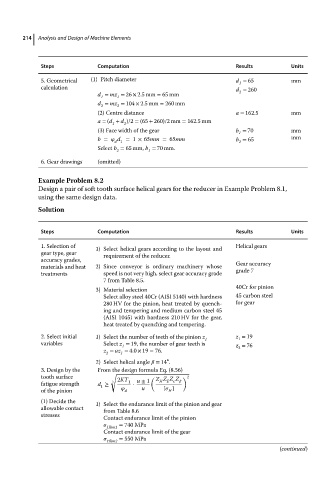
Steps Computation Results Units
5. Geometrical (1) Pitch diameter d = 65 mm
1
calculation d = 260
d = mz = 26 × 2.5 mm = 65 mm 2
1
1
d = mz = 104 × 2.5 mm = 260 mm
2 2
(2) Centre distance a = 162.5 mm
a = (d + d )/2 = (65 + 260)/2 mm = 162.5 mm
1
2
(3) Face width of the gear b = 70 mm
1
b = d =1 × 65mm =65mm b = 65 mm
d 1
2
Select b = 65 mm, b = 70 mm.
2
1
6. Gear drawings (omitted)
Example Problem 8.2
Design a pair of soft tooth surface helical gears for the reducer in Example Problem 8.1,
using the same design data.
Solution
Steps Computation Results Units
1. Selection of 1) Select helical gears according to the layout and Helical gears
gear type, gear requirement of the reducer.
accuracy grades, Gear accuracy
materials and heat 2) Since conveyor is ordinary machinery whose grade 7
treatments speed is not very high, select gear accuracy grade
7 from Table 8.5.
40Cr for pinion
3) Material selection
Select alloy steel 40Cr (AISI 5140) with hardness 45 carbon steel
280 HV for the pinion, heat treated by quench- for gear
ing and tempering and medium carbon steel 45
(AISI 1045) with hardness 210 HV for the gear,
heat treated by quenching and tempering.
2. Select initial 1) Select the number of teeth of the pinion z z = 19
1 1
variables Select z = 19, thenumberofgearteeth is
1 z = 76
2
z = uz = 4.0 × 19 = 76.
2 1
∘
2) Select helical angle = 14 .
3. Design by the From the design formula Eq. (8.56)
√
tooth surface 3 2KT u ± 1 ( Z Z Z Z )2
fatigue strength d ≥ 1 ⋅ H E
1 u [ ]
of the pinion d H
(1) Decide the 1) Select the endurance limit of the pinion and gear
allowable contact from Table 8.6
stresses
Contact endurance limit of the pinion
Hlim1 = 740 MPa
Contact endurance limit of the gear
Hlim2 = 550 MPa
(continued)