Page 313 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 313
7.14 BROMINE TRIFLUORIDE 293
Although detailed mechanistic studies are lacking, HSAB considerations appear to favor
the first non-redox mechanism, where sulfur, a soft nucleophile, attacks bromine, a soft
electrophile.
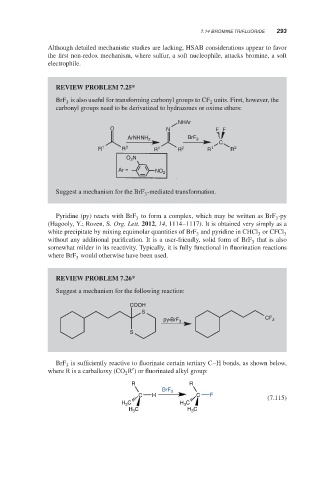
REVIEW PROBLEM 7.25*
BrF is also useful for transforming carbonyl groups to CF units. First, however, the
3
2
carbonyl groups need to be derivatized to hydrazones or oxime ethers:
NHAr
O N FF
BrF
ArNHNH 2 3
C
R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2
O 2 N
Ar = NO 2
Suggest a mechanism for the BrF -mediated transformation.
3
Pyridine (py) reacts with BrF to form a complex, which may be written as BrF ⋅py
3
3
(Hagooly, Y.; Rozen, S. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1114–1117). It is obtained very simply as a
white precipitate by mixing equimolar quantities of BrF and pyridine in CHCl or CFCl 3
3
3
without any additional purification. It is a user-friendly, solid form of BrF that is also
3
somewhat milder in its reactivity. Typically, it is fully functional in fluorination reactions
where BrF would otherwise have been used.
3
REVIEW PROBLEM 7.26*
Suggest a mechanism for the following reaction:
COOH
S
py•BrF 3 CF 3
S
BrF is sufficiently reactive to fluorinate certain tertiary C–H bonds, as shown below,
3
′
where R is a carbalkoxy (CO R ) or fluorinated alkyl group:
2
R R
BrF 3
C H C F
(7.115)
H C H 3 C
3
C C
H 3 H 3