Page 308 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 308
THE HALOGENS
288
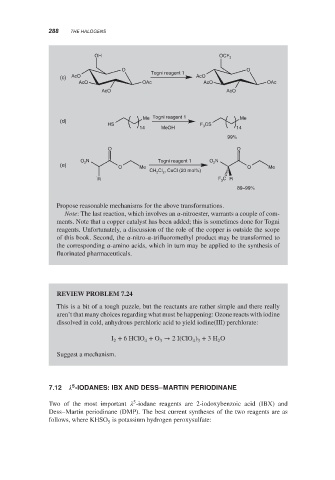
OH OCF 3
O Togni reagent 1 O
(c) AcO AcO
AcO OAc AcO OAc
AcO AcO
Me Togni reagent 1 Me
(d)
HS F 3 CS
14 MeOH 14
99%
O O
O N Togni reagent 1 O 2 N
(e) 2
O Me O Me
CH Cl , CuCl (20 mol%)
2
2
R F C R
3
89–99%
Propose reasonable mechanisms for the above transformations.
Note: The last reaction, which involves an -nitroester, warrants a couple of com-
ments. Note that a copper catalyst has been added; this is sometimes done for Togni
reagents. Unfortunately, a discussion of the role of the copper is outside the scope
of this book. Second, the -nitro- -trifluoromethyl product may be transformed to
the corresponding -amino acids, which in turn may be applied to the synthesis of
fluorinated pharmaceuticals.
REVIEW PROBLEM 7.24
This is a bit of a tough puzzle, but the reactants are rather simple and there really
aren’t that many choices regarding what must be happening: Ozone reacts with iodine
dissolved in cold, anhydrous perchloric acid to yield iodine(III) perchlorate:
I + 6HClO + O → 2I(ClO ) + 3H O
3
2
2
4 3
4
Suggest a mechanism.
5
7.12 -IODANES: IBX AND DESS–MARTIN PERIODINANE
5
Two of the most important -iodane reagents are 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) and
Dess–Martin periodinane (DMP). The best current syntheses of the two reagents are as
follows, where KHSO is potassium hydrogen peroxysulfate:
5