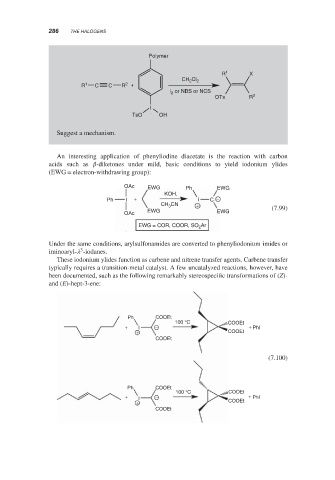
Page 306 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 306
THE HALOGENS
286
Polymer
R 1 X
Cl
CH 2 2
2
R 1 C C R +
l or NBS or NCS
2
OTs R 2
I
TsO OH
Suggest a mechanism.
An interesting application of phenyliodine diacetate is the reaction with carbon
acids such as -diketones under mild, basic conditions to yield iodonium ylides
(EWG = electron-withdrawing group):
OAc EWG Ph EWG
KOH,
Ph I + I C −
CN
CH 3 +
EWG EWG (7.99)
OAc
EWG = COR, COOR, SO 2 Ar
Under the same conditions, arylsulfonamides are converted to phenyliodonium imides or
3
iminoaryl- -iodanes.
These iodonium ylides function as carbene and nitrene transfer agents. Carbene transfer
typically requires a transition-metal catalyst. A few uncatalyzed reactions, however, have
been documented, such as the following remarkably stereospecific transformations of (Z)-
and (E)-hept-3-ene:
Ph COOEt
100 °C COOEt
+ I − + Phl
+ COOEt
COOEt
(7.100)
Ph COOEt
100 °C COOEt
+ I − + Phl
+ COOEt
COOEt