Page 305 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 305
3
7.11 -IODANES 285
−
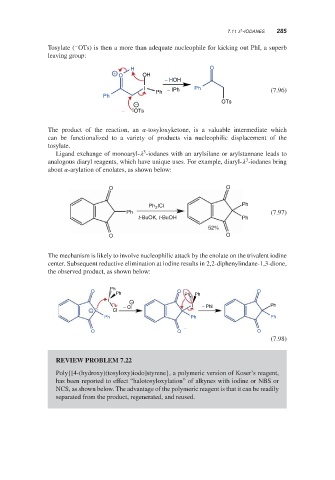
Tosylate ( OTs) is then a more than adequate nucleophile for kicking out PhI, a superb
leaving group:
H O
+ O OH
− HOH
I − IPh Ph
Ph (7.96)
Ph
− OTs
OTs
The product of the reaction, an -tosyloxyketone, is a valuable intermediate which
can be functionalized to a variety of products via nucleophilic displacement of the
tosylate.
3
Ligand exchange of monoaryl- -iodanes with an arylsilane or arylstannane leads to
3
analogous diaryl reagents, which have unique uses. For example, diaryl- -iodanes bring
about -arylation of enolates, as shown below:
O O
Ph 2 ICI Ph
Ph (7.97)
t-BuOK, t-BuOH Ph
52%
O O
The mechanism is likely to involve nucleophilic attack by the enolate on the trivalent iodine
center. Subsequent reductive elimination at iodine results in 2,2-diphenylindane-1,3-dione,
the observed product, as shown below:
Ph
O O O
Ph Ph Ph
I −
− Cl I − Phl Ph
− Cl
Ph Ph Ph
O O O
(7.98)
REVIEW PROBLEM 7.22
Poly{[4-(hydroxy)(tosyloxy)iodo]styrene}, a polymeric version of Koser’s reagent,
has been reported to effect “halotosyloxylation” of alkynes with iodine or NBS or
NCS, as shown below. The advantage of the polymeric reagent is that it can be readily
separated from the product, regenerated, and reused.