Page 147 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 147
128 w Chapter Eleven
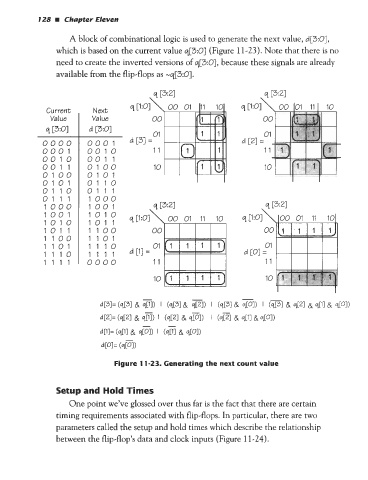
A block of combinational logic is used to generate the next value, d[3:0],
which is based on the current value q[3:O] (Figure 11-23). Note that there is no
need to create the inverted versions of q[3:O], because these signals are already
available from the flip-flops as -q[3:0].
Current Next
Value Value
q [3:01 d [3:0]
0000 000 1
000 1 0010
0010 001 1
001 1 0100
0100 0101
0101 01 10
01 10 01 11
01 11 1000
1000 1001
1001 I010 q[I:Olh 00, 01 , 11 , IO,
I010 101 1
101 1 1100
1100 1101
1101 11 10 01
11 10 1111 d [I] =
1111 0000 111 I I I I
10 1
Figure 1 1-23. Generating the next count value
Setup and Hold Times
One point we’ve glossed over thus far is the fact that there are certain
timing requirements associated with flip-flops. In particular, there are two
parameters called the setup and hold times which describe the relationship
between the flip-flop’s data and clock inputs (Figure 11-24).