Page 75 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 75
3.1 Introduction 51
Oleic acid
O
OH
H 2 O
Hydratase
OH
OH
NAD+ O
ADH
NADH
O
OH
O
NADPH NADPH
BVMO from P. putida BVMO from P. fluorescence
NADP + NADP +
O
O OH
OH
O
O O
O
H 2 O O
Esterase H 2
Esterase
OH
OH
O
n-Nonanoic acid n-Octanol
+ +
O
HO OH
OH
HO
O
O
ω-Hydroxynonanoic acid 1,10-Decanedioic acid
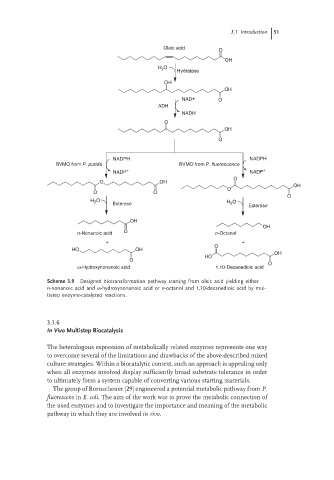
Scheme 3.9 Designed biotransformation pathway starting from oleic acid yielding either
n-nonanoic acid and ω-hydroxynonanoic acid or n-octanol and 1,10-decanedioic acid by mul-
tistep enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
3.1.6
In Vivo Multistep Biocatalysis
The heterologous expression of metabolically related enzymes represents one way
to overcome several of the limitations and drawbacks of the above-described mixed
culture strategies. Within a biocatalytic context, such an approach is appealing only
when all enzymes involved display sufficiently broad substrate tolerance in order
to ultimately form a system capable of converting various starting materials.
The group of Bornscheuer [29] engineered a potential metabolic pathway from P.
fluorescens in E. coli. The aim of the work was to prove the metabolic connection of
the used enzymes and to investigate the importance and meaning of the metabolic
pathway in which they are involved in vivo.