Page 76 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 76
52 3 Monooxygenase-Catalyzed Redox Cascade Biotransformations
The authors were able to heterologously express all three enzymes of pathway 2
(Scheme 3.10) in E. coli. In spite of their low expression levels, secondary alcohols
were successfully converted to primary alcohols after degradative cleavage of two
carbons (as acetic acid) via intermediate oxidation to ketone and Baeyer–Villiger
rearrangement to the corresponding ester. With this finding, they could show
that the three enzymes were metabolically connected and that the proposed
subterminal oxidation pathway was most probably responsible for the degradation
of alkanes in bacteria. This work represents an elegant example of in vivo multistep
biocatalysis. However, the biotransformations were based on enzymes that were
already metabolically related. Additionally, the reaction sequences were performed
solelyonananalyticalscale.
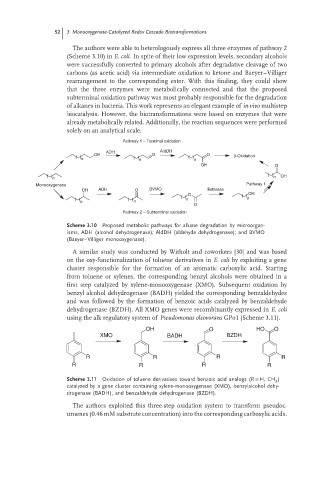
Pathway 1 – Terminal oxidation
ADH AIdDH
OH O O β-Oxidation
n n n
OH O
n n OH
Monooxygenase Pathway 1
OH ADH O BVMO Esterase
O OH
n n
n n
O
Pathway 2 – Subterminal oxidation
Scheme 3.10 Proposed metabolic pathways for alkane degradation by microorgan-
isms, ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase); AldDH (aldehyde dehydrogenase); and BVMO
(Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenase).
A similar study was conducted by Witholt and coworkers [30] and was based
on the oxy-functionalization of toluene derivatives in E. coli by exploiting a gene
cluster responsible for the formation of an aromatic carboxylic acid. Starting
from toluene or xylenes, the corresponding benzyl alcohols were obtained in a
first step catalyzed by xylene-monooxygenase (XMO). Subsequent oxidation by
benzyl alcohol dehydrogenase (BADH) yielded the corresponding benzaldehydes
and was followed by the formation of benzoic acids catalyzed by benzaldehyde
dehydrogenase (BZDH). All XMO genes were recombinantly expressed in E. coli
using the alk regulatory system of Pseudomonas oleovorans GPo1 (Scheme 3.11).
OH O HO O
XMO BADH BZDH
R R R R
R R R R
Scheme 3.11 Oxidation of toluene derivatives toward benzoic acid analogs (R = H, CH )
3
catalyzed by a gene cluster containing xylene-monooxygenase (XMO), benzylalcohol dehy-
drogenase (BADH), and benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (BZDH).
The authors exploited this three-step oxidation system to transform pseudoc-
umenes (0.46 mM substrate concentration) into the corresponding carboxylic acids.