Page 121 -
P. 121
94 CHAPTER 3 / A TOP-LEVEL VIEW OF COMPUTER FUNCTION
Time Time
Address Data
Address Data and address
(1st cycle) (2nd cycle)
sent by master
in same cycle over
Write (multiplexed) operation
Data separate bus lines.
Write (non-multiplexed) operation
Access
Address Data
time
Read (multiplexed) operation Time
Address
Data Data
Address Data
read write
Read-modify-write operation Read (non-multiplexed) operation
Data Data
Address
write read
Read-after-write operation
Address Data Data Data
Block data transfer
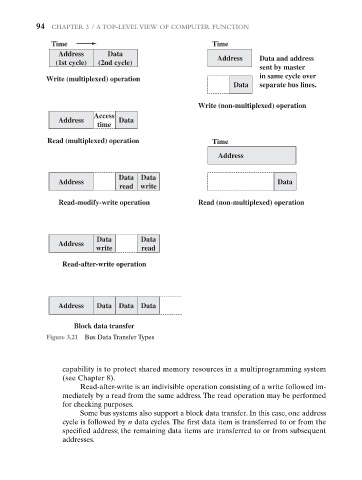
Figure 3.21 Bus Data Transfer Types
capability is to protect shared memory resources in a multiprogramming system
(see Chapter 8).
Read-after-write is an indivisible operation consisting of a write followed im-
mediately by a read from the same address. The read operation may be performed
for checking purposes.
Some bus systems also support a block data transfer. In this case, one address
cycle is followed by n data cycles. The first data item is transferred to or from the
specified address; the remaining data items are transferred to or from subsequent
addresses.