Page 467 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 467
452 Chapter 10 Digital Systems
For an asynchronous combinational circuit to operate properly, it must be free
of hazards—i.e., a signal should not make temporary transitions when it is
required to be stable, or change more than once when it is required to change only
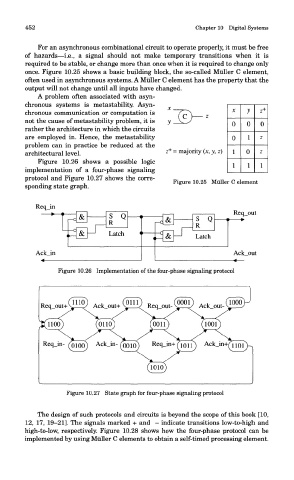
once. Figure 10.25 shows a basic building block, the so-called Miiller C element,
often used in asynchronous systems. A Miiller C element has the property that the
output will not change until all inputs have changed.
A problem often associated with asyn-
chronous systems is metastability. Asyn-
chronous communication or computation is
not the cause of metastability problem, it is
rather the architecture in which the circuits
are employed in. Hence, the metastability
problem can in practice be reduced at the
architectural level.
Figure 10.26 shows a possible logic
implementation of a four-phase signaling
protocol and Figure 10.27 shows the corre-
Figure 10.25 Miiller C element
sponding state graph.
Figure 10.26 Implementation of the four-phase signaling protocol
Figure 10.27 State graph for four-phase signaling protocol
The design of such protocols and circuits is beyond the scope of this book [10,
12, 17, 19-21]. The signals marked + and - indicate transitions low-to-high and
high-to-low, respectively. Figure 10.28 shows how the four-phase protocol can be
implemented by using Miiller C elements to obtain a self-timed processing element.