Page 168 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 168
HIGHEST PRIORITY LOWEST PRIORITY
INTrRRUPT
REQUEST
MICROPROCESSOR
lNTERRWT
ACKWWLEDGE
DATA 0US
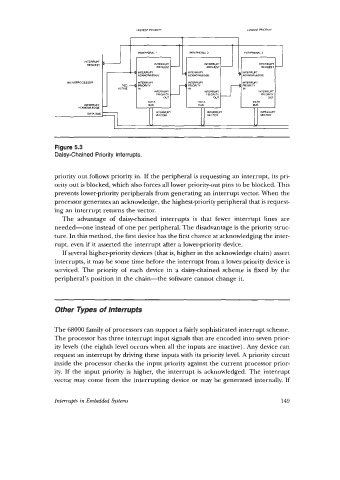
Figure 5.3
Daisychained Priority Interrupts.
priority out follows priority in. If the peripheral is requesting an interrupt, its pri-
ority out is blocked, which also forces all lower priority-out pins to be blocked. This
prevents lower-priority peripherals from generating an interrupt vector. When the
processor generates an acknowledge, the highest-priority peripheral that is request-
ing an interrupt returns the vector.
The advantage of daisy-chained interrupts is that fewer interrupt lines are
needed-one instead of one per peripheral. The disadvantage is the priority struc-
ture. In this method, the first device has the first chance at acknowledging the inter-
rupt, even if it asserted the interrupt after a lower-priority device.
If several higher-priority devices (that is, higher in the acknowledge chain) assert
interrupts, it may be some time before the interrupt from a lower-priority device is
serviced. The priority of each device in a daisychained scheme is fixed by the
peripheral’s position in the chain-the software cannot change it.
Other Types of Interrupts
The 68000 family of processors can support a fairly sophisticated interrupt scheme.
The processor has three interrupt input signals that are encoded into seven prior-
ity levels (the eighth level occurs when all the inputs are inactive). Any device can
request an interrupt by driving these inputs with its priority level. A priority circuit
inside the processor checks the input priority against the current processor prior-
ity. If the input priority is higher, the interrupt is acknowledged. The interrupt
vector may come from the interrupting device or may be generated internally. If
Interrupts in Embedded Systems 149