Page 171 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 171
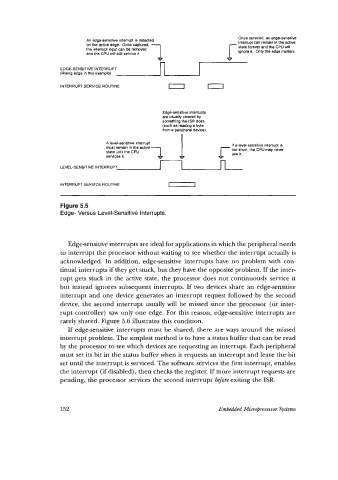
An edge-sensitive interrupt is deteded Once serviced. an edge-sensitive
interrupt can remain in the active
on the active edge. Once captured. a state forever and the CPU will
the intempt input can be remved h
ienore %. Only the edge matters.
and the CPU will still service it.
EDGE-SENSITIVE INTERRUPT
(Rising edge in this example)
INTERRUPT SERVICE ROUTINE 0 0
Edge-Sensitive interrupts
are usually cleared by
something the ISR does
(such as reading e byle
from a peripheral device).
A leveksensitive interrupt i s If a level-sensitive interrupt is
must remain in the active a too short, the CPU may never
state until the CPU see it.
services it.
INTERRUPT SERVICE ROUTINE 0
Figure 5.5
Edge- Versus Level-Sensitive Interrupts.
Edge-sensitive interrupts are ideal for applications in which the peripheral needs
to interrupt the processor without waiting to see whether the interrupt actually is
acknowledged. In addition, edge-sensitive interrupts have no problem with con-
tinual interrupts if they get stuck, but they have the opposite problem. If the inter-
rupt gets stuck in the active state, the processor does not continuously service it
but instead ignores subsequent interrupts. If two devices share an edge-sensitive
interrupt and one device generates an interrupt request followed by the second
device, the second interrupt usually will be missed since the processor (or inter-
rupt controller) saw only one edge. For this reason, edge-sensitive interrupts are
rarely shared. Figure 5.6 illustrates this condition.
If edge-sensitive interrupts must be shared, there are ways around the missed
interrupt problem. The simplest method is to have a status buffer that can be read
by the processor to see which devices are requesting an interrupt. Each peripheral
must set its bit in the status buffer when it requests an interrupt and leave the bit
set until the interrupt is serviced. The software services the first interrupt, enables
the interrupt (if disabled), then checks the register. If more interrupt requests are
pending, the processor services the second interrupt before exiting the ISR.
152 Embedded Mam@rocessm System