Page 348 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 348
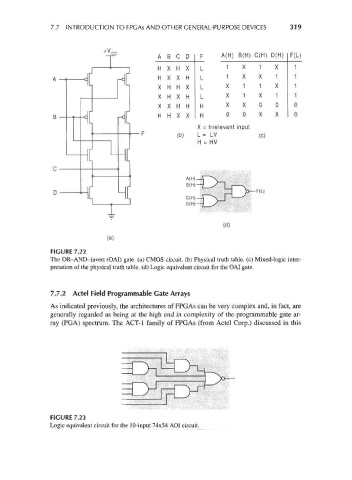
7.7 INTRODUCTION TO FPGAs AND OTHER GENERAL-PURPOSE DEVICES 319
A B C D F A(H) B(H) C(H) D(H) F(L)
H X H X L 1 X 1 X 1
H X X H L 1 X X 1 1
X H H X L X 1 1 X 1
X H X H L X 1 X 1 1
X X H H H X X 0 0 0
H H X X H 0 0 X X 0
X = Irrelevant input
(b) L = LV (c)
H = HV
A(H)
B(H)
JO— F(L)
x /
C(H)- ^ ' '
D(H)-
(d)
FIGURE 7.22
The OR-AND-invert (OAI) gate, (a) CMOS circuit, (b) Physical truth table, (c) Mixed-logic inter-
pretation of the physical truth table, (d) Logic equivalent circuit for the OAI gate.
7.7.2 Actel Field Programmable Gate Arrays
As indicated previously, the architectures of FPGAs can be very complex and, in fact, are
generally regarded as being at the high end in complexity of the programmable gate ar-
ray (PGA) spectrum. The ACT-1 family of FPGAs (from Actel Corp.) discussed in this
FIGURE 7.23
Logic equivalent circuit for the 10-input 74x54 AOI circuit.