Page 351 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 351
322 CHAPTER 7 / PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES
9 n D
?
1 1 1 1
IOB IOB IOB 108 ;
I/O 1 1 Ml
Pin "^\
N»
V ea -
O
s
\~ Switching Switching
Matrix
Matrix
^\-
Interconnect ^^ 1
Lines 1
A
-* 8 X _+. * — i »•
D- CO -> c CLB ^ — * CLB
O -> K
0 ^
Horizontal t t
long line
— Switching Switching
I/O — Matrix Matrix
Block ^\
4
n- I |
CD
0 —-* •> — * — l
-^ CLB _^ CLB
^r — «>•
—
Configurable t t
Logic — ^
Block ^
Switching Switching
Matrix Matrix
Ur- CQ
O
v I. in/ / L_J IK
Interconnect _/ Two vertical / \^ Global long
' ines long lines line
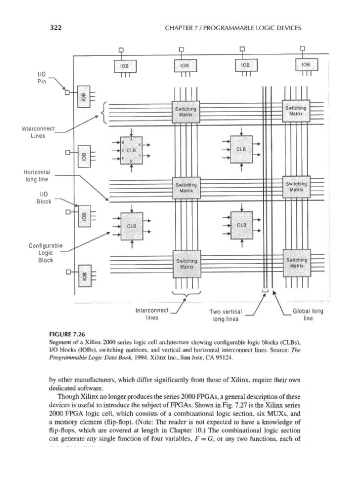
FIGURE 7.26
Segment of a Xilinx 2000 series logic cell architecture showing configurable logic blocks (CLBs),
I/O blocks (lOBs), switching matrices, and vertical and horizontal interconnect lines. Source: The
Programmable Logic Data Book, 1994. Xilinx Inc., San Jose, CA 95124.
by other manufacturers, which differ significantly from those of Xilinx, require their own
dedicated software.
Though Xilinx no longer produces the series 2000 FPGAs, a general description of these
devices is useful to introduce the subject of FPGAs. Shown in Fig. 7.27 is the Xilinx series
2000 FPGA logic cell, which consists of a combinational logic section, six MUXs, and
a memory element (flip-flop). (Note: The reader is not expected to have a knowledge of
flip-flops, which are covered at length in Chapter 10.) The combinational logic section
can generate any single function of four variables, F = G, or any two functions, each of