Page 353 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 353
324 CHAPTER 7 / PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES
To lOBs
Tri-state
driver
I/O Pin
Buffer
Flip-flop memory / I/O Clock
element
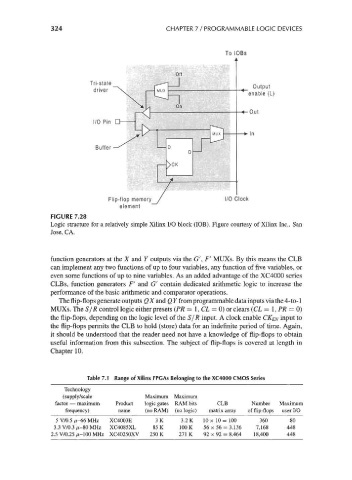
FIGURE 7.28
Logic structure for a relatively simple Xilinx I/O block (IOB). Figure courtesy of Xilinx Inc., San
Jose, CA.
function generators at the X and Y outputs via the G', ¥' MUXs. By this means the CLB
can implement any two functions of up to four variables, any function of five variables, or
even some functions of up to nine variables. As an added advantage of the XC4000 series
CLBs, function generators F' and G' contain dedicated arithmetic logic to increase the
performance of the basic arithmetic and comparator operations.
The flip-flops generate outputs QX and Q Y from programmable data inputs via the 4-to-1
MUXs. The S/R control logic either presets (PR=l,CL = 0) or clears (CL=l,PR = 0)
the flip-flops, depending on the logic level of the S/R input. A clock enable CK EN input to
the flip-flops permits the CLB to hold (store) data for an indefinite period of time. Again,
it should be understood that the reader need not have a knowledge of flip-flops to obtain
useful information from this subsection. The subject of flip-flops is covered at length in
Chapter 10.
Table 7.1 Range of Xilinx FPGAs Belonging to the XC4000 CMOS Series
Technology
(supply/scale Maximum Maximum
factor — maximum Product logic gates RAM bits CLB Number Maximum
frequency) name (no RAM) (no logic) matrix array of flip-flops user I/O
5 V/0.5 ^-66 MHz XC4003E 3K 3.2 K 10 x 10 = 100 360 80
3.3 V/0.3 /i-80 MHz XC4085XL 85 K 100 K 56 x 56 = 3,136 7,168 448
2.5 V/0.25 M-100 MHz XC40250XV 250 K 271 K 92 x 92 = 8,464 18,400 448