Page 354 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 354
7.7 INTRODUCTION TO FPGAs AND OTHER GENERAL-PURPOSE DEVICES 325
Control Inputs
C1 C2 C3 C4
i i 1 i
H1 Din S/R CK C
G4- -
Function PR
G3- D
generator r,
b Q •QY(H)
of
G1 to G4 H' t>
G1 CK C EN
Function CL
generator G " P
1
and
F4 H1
I—
Function U Din
Function
H generator _.
Generator
of F' PR
F1 to F4
G' •-DH Q •QX(H)
- H'
EN
CL
P
(clock)
MUXs controlled by
configuration program
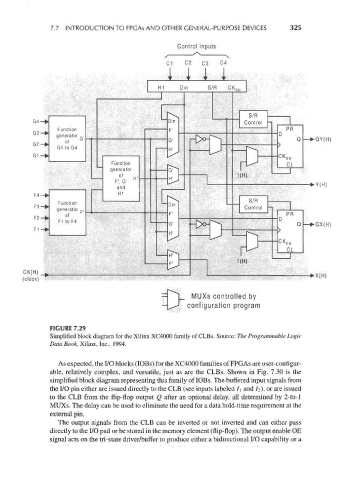
FIGURE 7.29
Simplified block diagram for the Xilinx XC4000 family of CLBs. Source: The Programmable Logic
Data Book, Xilinx, Inc., 1994.
As expected, the I/O blocks (lOBs) for the XC4000 families of FPGAs are user-configur-
able, relatively complex, and versatile, just as are the CLBs. Shown in Fig. 7.30 is the
simplified block diagram representing this family of lOBs. The buffered input signals from
the I/O pin either are issued directly to the CLB (see inputs labeled I\ and /2), or are issued
to the CLB from the flip-flop output Q after an optional delay, all determined by 2-to-l
MUXs. The delay can be used to eliminate the need for a data hold-time requirement at the
external pin.
The output signals from the CLB can be inverted or not inverted and can either pass
directly to the I/O pad or be stored in the memory element (flip-flop). The output enable OE
signal acts on the tri-state driver/buffer to produce either a bidirectional I/O capability or a