Page 463 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 463
10.4 THE BASIC MEMORY CELLS 433
observe the difference in the Q(H) waveform for these two types of basic cells. Clearly,
the set-dominant character is different from the reset-dominant character with regard to the
S, R = 1, 1 input condition. This difference may be regarded as the single most important
difference between these two memory cells and will play a role in the discussion that follows.
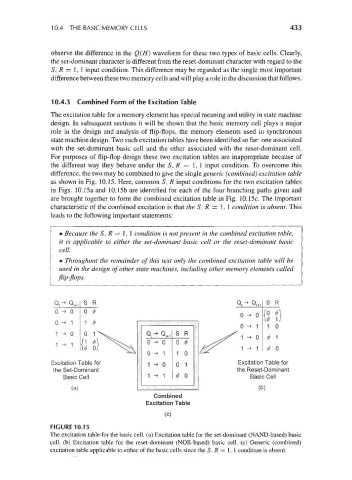
10.4.3 Combined Form of the Excitation Table
The excitation table for a memory element has special meaning and utility in state machine
design. In subsequent sections it will be shown that the basic memory cell plays a major
role in the design and analysis of flip-flops, the memory elements used in synchronous
state machine design. Two such excitation tables have been identified so far: one associated
with the set-dominant basic cell and the other associated with the reset-dominant cell.
For purposes of flip-flop design these two excitation tables are inappropriate because of
the different way they behave under the S, R = 1,1 input condition. To overcome this
difference, the two may be combined to give the single generic (combined) excitation table
as shown in Fig. 10.15. Here, common S, R input conditions for the two excitation tables
in Figs. 10.15a and 10.15b are identified for each of the four branching paths given and
are brought together to form the combined excitation table in Fig. 10.15c. The important
characteristic of the combined excitation is that the S, R = 1,1 condition is absent. This
leads to the following important statements:
• Because the S, R = 1, 1 condition is not present in the combined excitation table,
it is applicable to either the set-dominant basic cell or the reset-dominant basic
cell.
• Throughout the remainder of this text only the combined excitation table will be
used in the design of other state machines, including other memory elements called
flip-flops.
s R S R
0 0 0
*
0- 1 - ' • • -» ° l IWI 1 <
0 - 1 1 0
1 -» 0 0 1 S R 1 - 0 # 1
1 -> 1 0-^ 0 0 ^
0 1 - 1 ^ 0
0 1 0
Excitation Table for 0 0 1 Excitation Table for
the Set-Dominant the Reset-Dominant
Basic Cell 1 -» 1 ^ 0 Basic Cell
(a) (b)
Combined
Excitation Table
(c)
FIGURE 10.15
The excitation table for the basic cell, (a) Excitation table for the set-dominant (NAND-based) basic
cell, (b) Excitation table for the reset-dominant (NOR-based) basic cell, (c) Generic (combined)
excitation table applicable to either of the basic cells since the 5, R = 1, 1 condition is absent.