Page 735 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 735
14.10 DETECTION AND ELIMINATION OF TIMING DEFECTS 701
Q(H)
Q(L) —
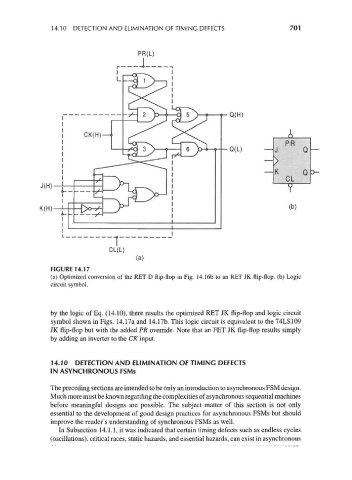
FIGURE 14.17
(a) Optimized conversion of the RET D flip-flop in Fig. 14.16b to an RET JK flip-flop, (b) Logic
circuit symbol.
by the logic of Eq. (14.10), there results the optimized RET JK flip-flop and logic circuit
symbol shown in Figs. 14.17a and 14.17b. This logic circuit is equivalent to the 74LS109
JK flip-flop but with the added PR override. Note that an FET JK flip-flop results simply
by adding an inverter to the CK input.
14.10 DETECTION AND ELIMINATION OF TIMING DEFECTS
IN ASYNCHRONOUS FSMs
The preceding sections are intended to be only an introduction to asynchronous FSM design.
Much more must be known regarding the complexities of asynchronous sequential machines
before meaningful designs are possible. The subject matter of this section is not only
essential to the development of good design practices for asynchronous FSMs but should
improve the reader's understanding of synchronous FSMs as well.
In Subsection 14.1.1, it was indicated that certain timing defects such as endless cycles
(oscillations), critical races, static hazards, and essential hazards, can exist in asynchronous