Page 737 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 737
14.10 DETECTION AND ELIMINATION OF TIMING DEFECTS 703
interconnected states P, Q, R, S, P. In this case an endless cycle exists if
fpQ • /OR • fits • fsp + 0. (14.12)
14.10.2 Races and Critical Races
The set of alternative cycle paths that lead to the same state is called a race. Recall that this
subject was discussed in Section 11.2 relative to output race glitches (ORGs) in synchronous
FSMs. In an asynchronous FSM a race results when the FSM undergoes a transition to a
next state that differs from the present state by two or more bits. There are n \ race paths for
a race condition involving the change of n state variables. Since no two feedback variables
can change precisely at the same time, one variable will always change before another, even
though the time span between the two events may be very small. Thus, the alternative race
path taken by the FSM will depend on which feedback variable changes first to meet the
stability criterion of Eq. (14.3), and this is not usually predictable.
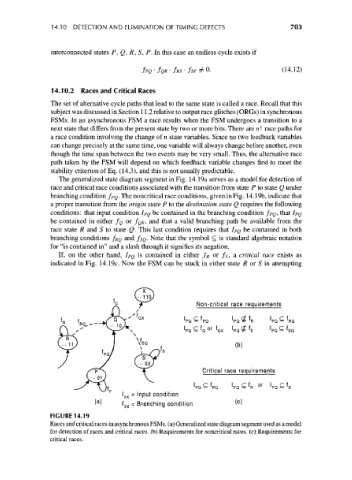
The generalized state diagram segment in Fig. 14.19a serves as a model for detection of
race and critical race conditions associated with the transition from state P to state Q under
branching condition f PQ. The noncritical race conditions, given in Fig. 14.19b, indicate that
a proper transition from the origin state P to the destination state Q requires the following
conditions: that input condition IPQ be contained in the branching condition /PQ, that I PQ
be contained in either /g or f QX, and that a valid branching path be available from the
race state R and S to state Q. This last condition requires that IPQ be contained in both
branching conditions f RQ and f$Q. Note that the symbol c is standard algebraic notation
for "is contained in" and a slash through it signifies its negation.
If, on the other hand, I PQ is contained in either f R or /$, a critical race exists as
indicated in Fig. 14.19c. Now the FSM can be stuck in either state R or S in attempting
Non-critical race requirements
'PQ — 'PQ 'PQ ^ *R 'PQ — 'RQ
'PQ — 'Q or 'QX 'PQ ? 's 'PQ — 'SQ
(b)
Critical race requirements
f or f
lp Q £fp Q ' PQ £ R 'pQ£ s
, xx = Input condition
a c
( ) f xx = Branching condition ( '
FIGURE 14.19
Races and critical races in asynchronous FSMs. (a) Generalized state diagram segment used as a model
for detection of races and critical races, (b) Requirements for noncritical races, (c) Requirements for
critical races.